#human-evolution
#human-evolution
[ follow ]
#neanderthals #denisovans #ancient-dna #paleoanthropology #archaeology #genetics #paleontology #anthropology
fromMail Online
22 hours agoWhy women's breasts are so large compared to other animals, revealed
Human breasts sit at an elevated temperature, protecting a newborn from hypothermia. What's more, the size and shape of the breast allows for broad contact surface - enhancing the heat transfer from mother to child. This could improve a newborn's chances of survival and provide an evolutionarily grounded explanation for the development of external breasts in humans.
Science
Science
fromenglish.elpais.com
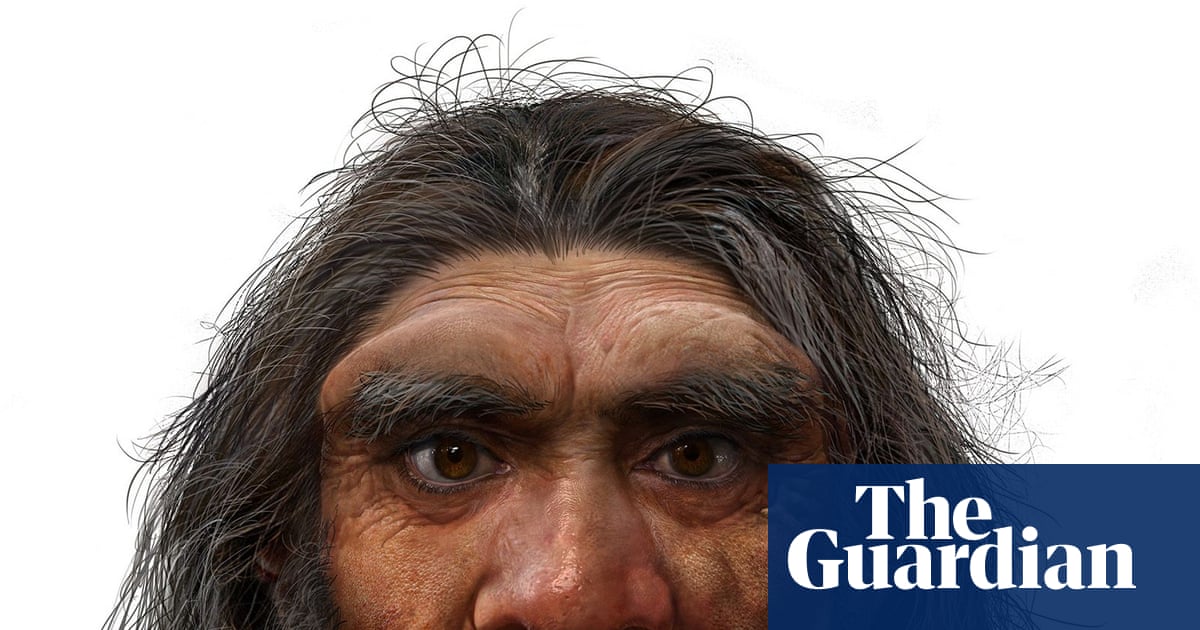
1 week agoLudovic Slimak on Neanderthals: It was suicide. Humans disappear when they no longer want to live because their values have collapsed'
Neanderthals, despite cultural complexity and interbreeding, went extinct around 42,000 years ago, likely due to isolation and abandonment while Homo sapiens prevailed.
fromPsychology Today
2 weeks agoThe Digital Savanna
Somewhere between six and seven million years ago, our ancestors began walking upright, and the advantages were considerable: Freed from locomotion, upper limbs could grasp, manipulate, eventually craft, and the opposable thumb became the hinge on which human civilization would turn. We are, above all else, tool users-fire, the wheel, writing, the printing press, the transistor-each tool reshaping not only what we could do but who we became.
Artificial intelligence
fromBig Think
4 months agoThe ancient origins of partnering and romantic love
No matter what their gods were, what they did for a living, what they wore, the songs they sang, everything varies except love, and everybody loves. So I became convinced that this was a real thing, that we were built somehow to form partnerships. And then the day came when I thought to myself, "Well, then it must be something in the brain."
Relationships
fromenglish.elpais.com
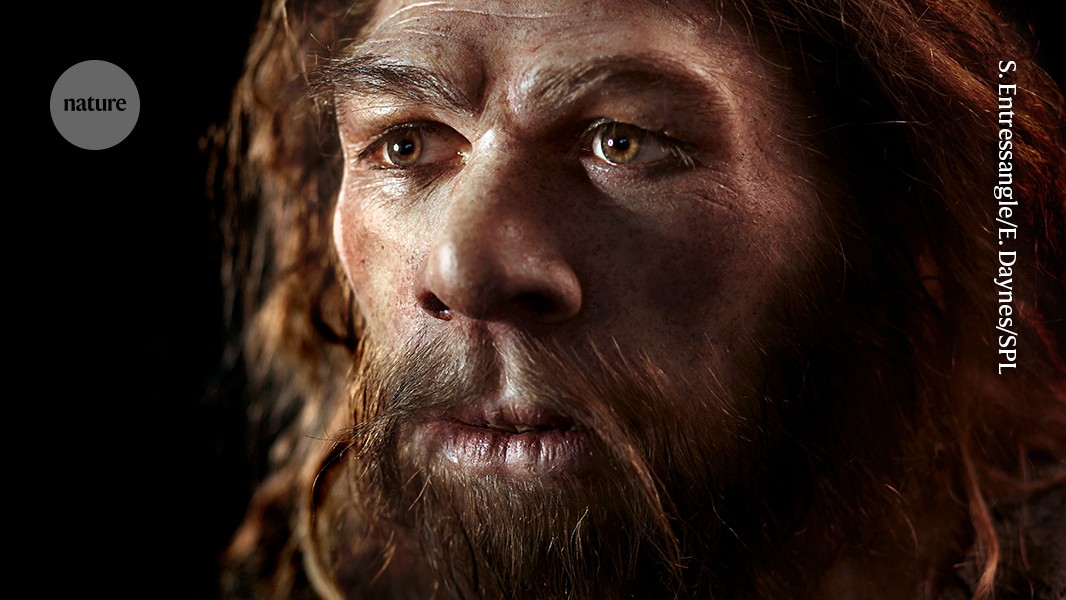
4 months agoSvante Paabo, father of paleogenetics: The reason for the Neanderthals' extinction lies in how numerous we've become'
Geneticist Svante Paabo demonstrated that DNA can be extracted from human fossils that are thousands of years old. His team was the first to sequence the complete genome of Neanderthals, our closest human relatives, and discovered that Homo Sapiens had sex and children with them. He also revealed the existence of a third, previously unknown human lineage, the Denisovans, thanks to genetic material extracted from a tiny bone of a girl who lived in a Siberian cave some 50,000 years ago.
Science
fromMail Online
4 months agoScientists discover autism may be a natural part of human evolution
But now US researchers say that natural selection could have given rise to autism-associated genes, with behaviours associated with the disorder generally involving cognitive traits that are unique to humans. Writing in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, experts at Stanford University discovered that the most abundant type of outer-layer brain neurons-called L2/3 IT neurons-evolved exceptionally quickly in humans compared to other mammals.
Science
fromThe Atlantic
6 months agoWas Language a Parental Invention?
If you have spent time with an infant, you might recognize the scene: A child is wailing, inconsolable, and you, the parent, have to go to the bathroom. Or eat. Or attend to a pot that's boiling over. But someone needs to watch the baby. Such urgent situations often call for innovation. In modern times, we might negotiate schedules with our partners, seek out affordable child care, or purchase "baby-tainment" contraptions via our phones.
Science
fromwww.theguardian.com
6 months agoThe Origin of Language by Madeleine Beekman review the suprising history of speech
Language likely evolved as a crucial tool to facilitate the care of vulnerable infants, requiring cooperative parenting and communication among groups in early human societies.
philosophy
fromwww.esquire.com
6 months ago'Alien: Earth' Review: Xenomorphs Are Must-Watch Horror Again
When Alien: Earth hits FX on August 12, prepare to ask yourself all kinds of wonderful questions, such as: Are our human bodies not a kind of outdated machine? Are the aliens not just a biological inevitability that we don't yet understand?
Television
fromThe Washington Post
6 months agoThis gene tweak in mice offers clues to what sets us apart from Neanderthals
The modern form of the gene ADSL in humans reduces enzyme stability compared to that found in Neanderthals or Denisovans, suggesting significant biochemical differences between species.
Science
Mental health
fromArchDaily
10 months agoBiophilic Architecture without Plants: Invisible Design for Wellbeing
True biophilic design extends beyond greenery, emphasizing a deeper human-nature connection that influences architectural space.
Biophilia reflects our evolutionary reliance on natural elements, shaping health-enhancing design strategies.
[ Load more ]