fromwww.scientificamerican.com
1 month agoMeet the Ancestor That Connects Us to Neandertals and Denisovans
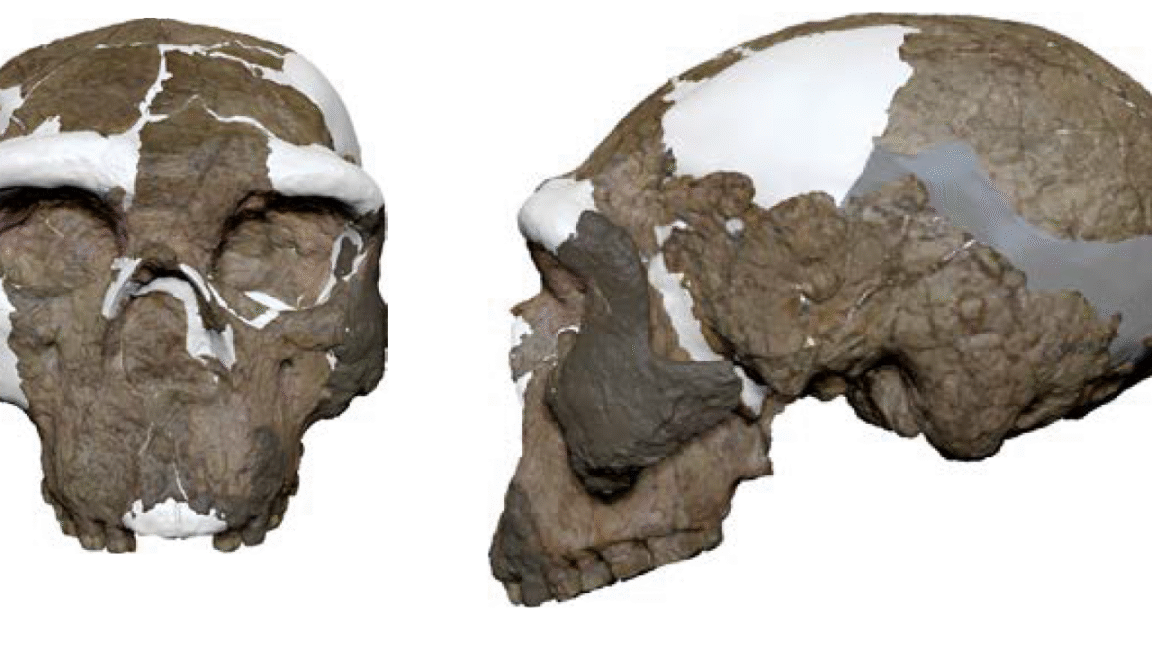
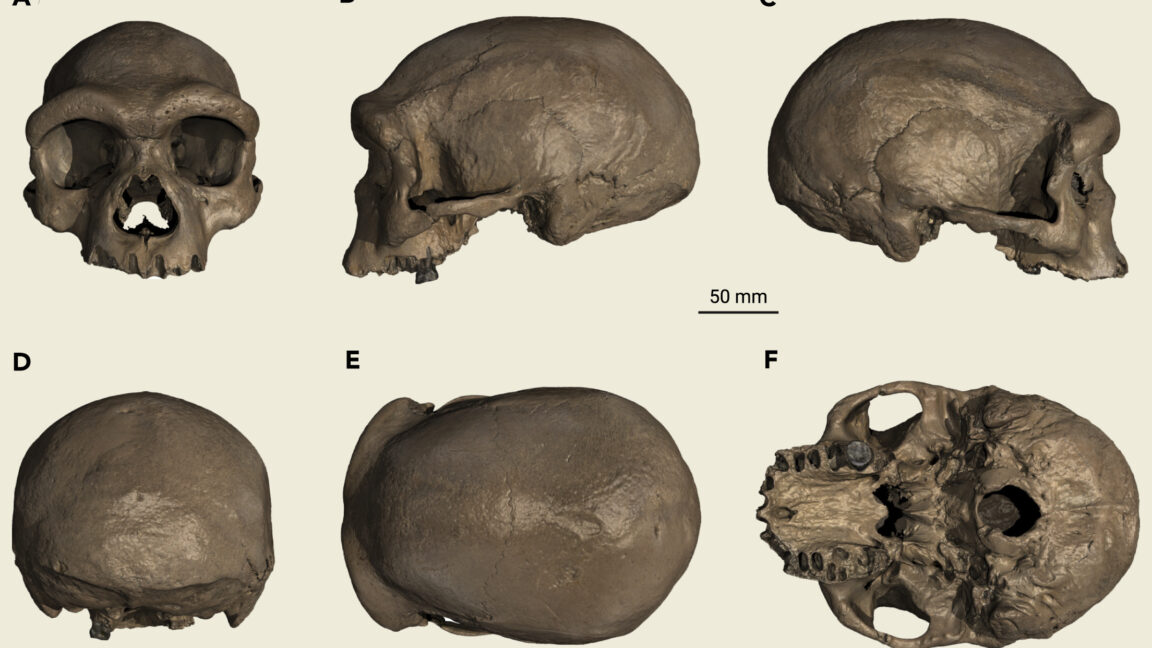
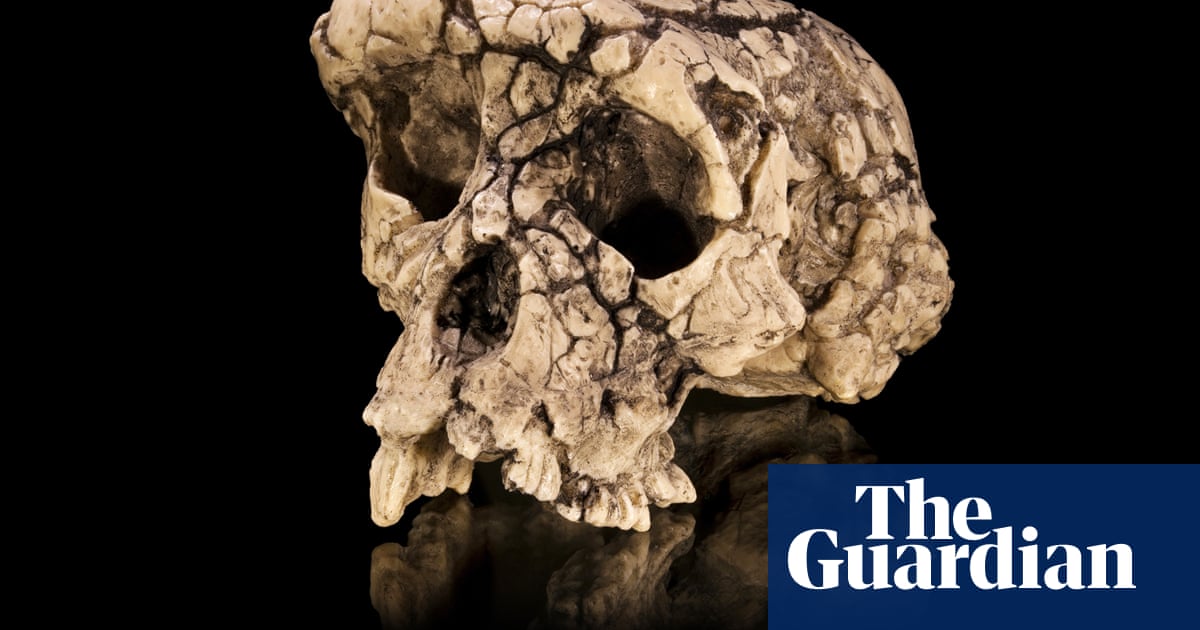
New research published today in Nature dates the boneschipped out from a cave called Grotte a Hominides and nearby it over decadesto about 773,000 years ago, during the era of the last common ancestor of Homo sapiens, Homo neanderthalensis and Denisovans (a group of humans that ranged across Asia and that does not have an agreed-upon species name). We can say that the shared ancestry between these three species is perhaps in Grotte a Hominides in Casablanca, says study co-author Abderrahim Mohib, a prehistorian at the National Institute of Archaeology and Heritage Sciences in Rabat, Morocco.