"Philosophers and scientists have looked into consciousness, leading to various theories, yet empirical support often shows confirmation bias based on methodological choices."
"The collaboration tested two significant theories of consciousness, IIT and GNWT, to create a baseline for experimental predictions that could advance our understanding."
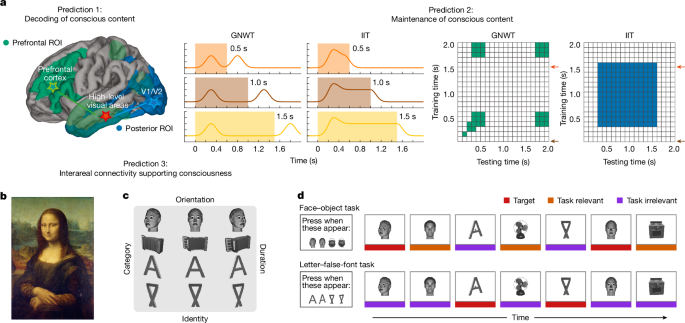
The article examines how philosophers and scientists have been wrestling with the nature of consciousness and its relation to physical brain processes. This investigation has produced several competing theories, with varying empirical support influenced by methodological choices, suggesting a confirmation bias in theory testing. To facilitate progress, a large-scale adversarial collaboration was initiated to test two dominant theories: Integrated Information Theory (IIT) and Global Neuronal Workspace Theory (GNWT). The collaborative effort aimed to identify predictions of the theories and develop a clear experimental framework for testing them.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]