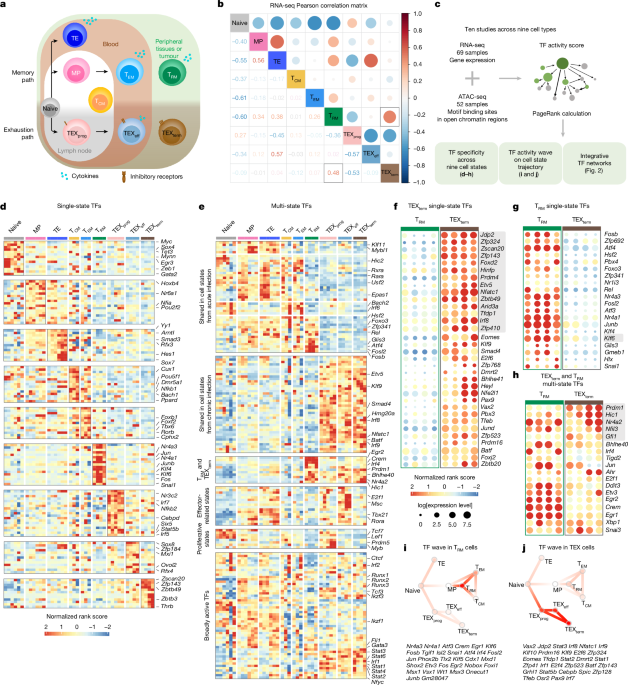
"Cell states are the range of cellular phenotypes arising from a defined cell type's interaction with its environment. Within the immune system, T cells possess several differentiation states, particularly as naive T cells differentiate into diverse states with different functionalities and trafficking patterns in various immune environments, such as tumours and virus infections. As transcription factors (TFs) govern cell state differentiation14, understanding how TFs shape these states is essential for programming beneficial states with therapeutic potential."
"Many studies show that TILs with T RM cell characteristics correlate with better survival in patients with solid tumours9,10,11,12,13. Conversely, during persistent antigen stimulation scenarios such as chronic virus infection (for example, HIV) or cancer, T cells progressively express diverse inhibitory receptors, including PD1, and lose memory potential and effector functions. This process is known as T cell exhaustion (TEX), and cells in this trajectory eventually adopt the TEX term cell state."
Cell states encompass cellular phenotypes shaped by interactions with the environment. Naive T cells differentiate into multiple states with distinct functions and trafficking across tissues and infections. Transcription factors govern state differentiation and are crucial for programming therapeutic T cell states. Engineering CD8+ T cells for adoptive transfer or CAR-T therapy could improve anti-tumor responses. Identifying TFs controlling CD8+ T cell states is challenging due to heterogeneity and overlapping transcriptomes between divergent functional states. The protective tissue-resident memory (TRM) state and the dysfunctional terminally exhausted (TEXterm) state are transcriptionally similar but functionally opposite. TEXterm cells express multiple inhibitory receptors, lack effector and proliferative capacity, and resist PD1 blockade; high TEXterm marker expression correlates with poor prognosis.
#cd8-t-cells #transcription-factors #t-cell-exhaustion #tissue-resident-memory #adoptive-cell-therapy
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]