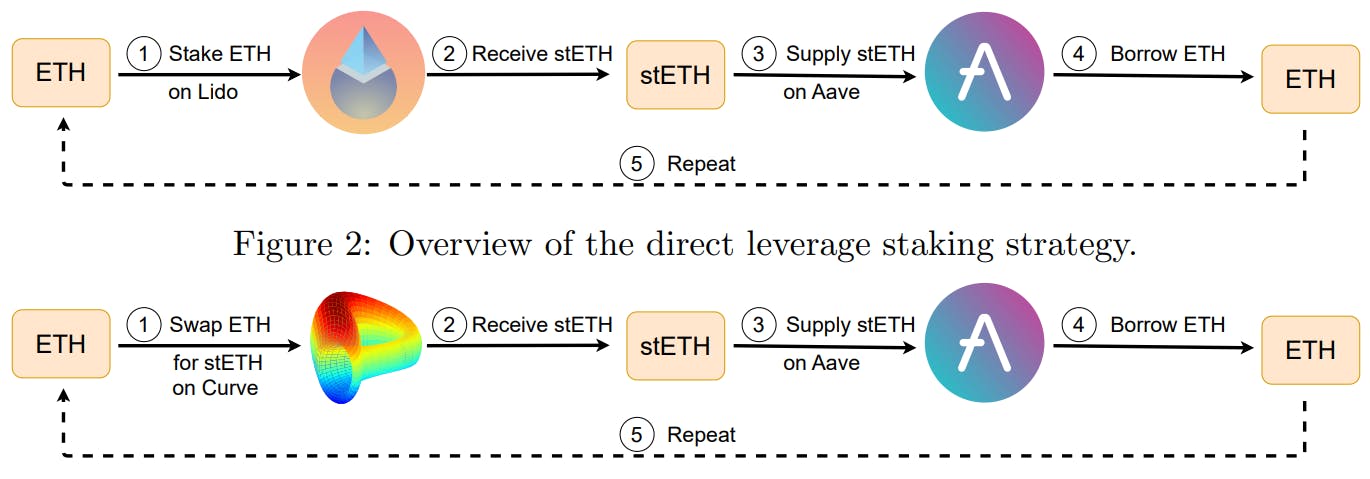
"Leverage borrowing allows users to amplify their investment positions on Ethereum by iterative cycles of swapping, depositing, and borrowing assets through decentralized exchanges."
"Liquid Staking Providers enable users to stake their tokens on platforms like Lido to earn derivatives, which can be used for trading, collateralized borrowing, and liquidity provision."
"The section compares three leverage staking strategies: leverage borrowing, direct leverage staking, and indirect leverage staking, highlighting their unique characteristics and application."
"In a liquid staking ecosystem, understanding the roles of system participants is essential for grasping the dynamics of Ethereum's DeFi landscape, particularly in leveraging staking options."
Liquid staking on Ethereum allows users to stake native tokens on platforms like Lido, receiving liquid staking derivatives (LSDs) such as stETH. These LSDs can be utilized in various financial activities, including trading and collateralized borrowing. Different leverage staking strategies are identified, including leverage borrowing, which involves iterative exchanges between assets to increase leverage. Understanding the roles of different system participants enhances the comprehension of the DeFi landscape and the mechanics of liquidity provision and staking activities in Ethereum's ecosystem.
Read at Hackernoon
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]