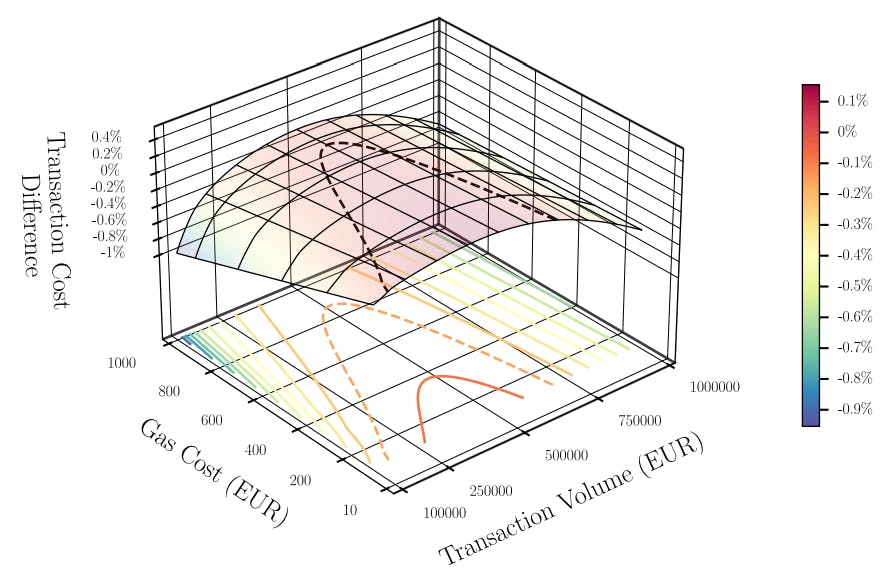
"The implementation of our simulations, reflected in the total costs of CBDC swaps, emphasizes how critical liquidity provision and fee structures impact transaction efficiency."
"By calibrating our analysis on historical FM rates and assessing AMM pool compositions, we provide nuanced insights into the efficiency of decentralized exchanges."
The article presents a detailed analysis of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) exchange costs concerning the Swiss Franc, Euro, and Singaporean Dollar. It systematically compares the L1-Mariana with L2-L3-Exchange systems, underpinning different liquidity setups for token pools. Historical exchange rates were used to qualitatively measure price impacts and liquidity provisions, with a focus on liquidity pool structures and associated costs, such as gas fees. The findings illustrate how liquidity management fundamentally influences transaction efficiencies in decentralized finance (DeFi).
Read at Hackernoon
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]