#innate-immunity
#innate-immunity
[ follow ]
fromNature
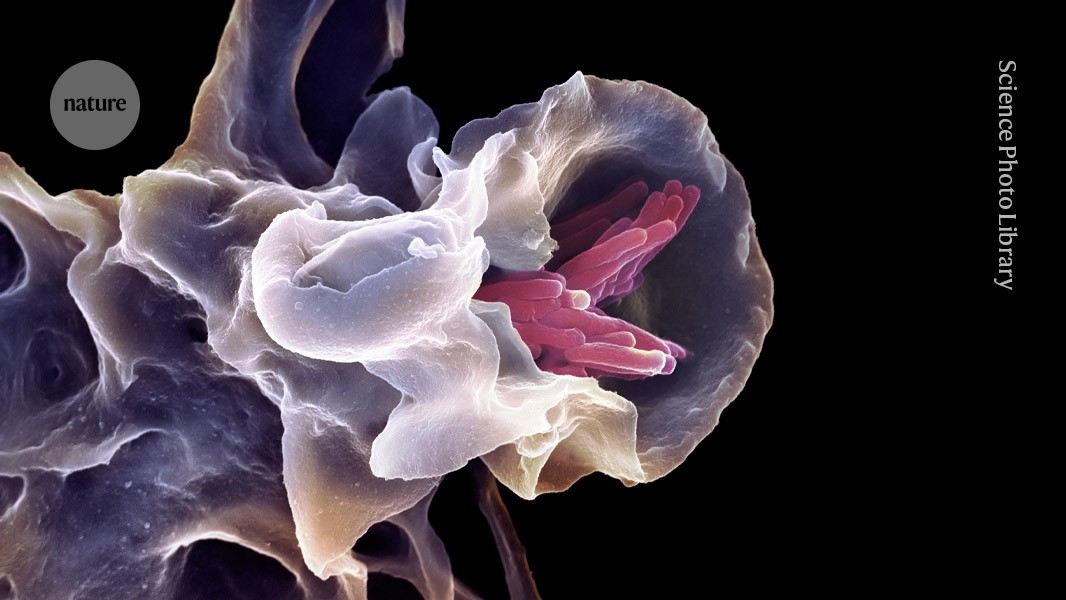
1 month agoPtdIns(3,5)P2 is an endogenous ligand of STING in innate immune signalling - Nature
Exposure to cytosolic DNA triggers innate immune responses through cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS)1,2,3. After binding to DNA, cGAS produces cGAMP as a second messenger that binds to stimulator of interferon genes (STING), a signalling adaptor protein anchored to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)3,4,5. STING then traffics from the ER through the Golgi to perinuclear vesicle clusters, which leads to activation of the kinases TBK1 and IKK and subsequent induction of interferons and other cytokines6,7,8,9.
Science
fromNature
3 months agoThis scientist found a new trick of the immune system by digging through cellular rubbish
From her office at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel, she holds up a blue plastic model of a proteasome, a barrel-shaped structure with a hollow core. The function seems simple: proteins enter the chamber, where they are shredded and then exit as smaller peptide fragments. But the machinery is surprisingly elaborate. The core comprises more than two dozen protein subunits and can associate with a variety of regulatory caps.
Science
fromwww.scientificamerican.com
4 months agoCells Have a Death Switch That Protects Us from Viruses but Also Leads to Aging
Now researchers have discovered that a special group of about 100 immune proteins hangs out inside every cell in the body, where these proteins do nothing but wait. Then, when a virus breaks in, it seeds a crystal, and the proteins instantly clump around it, forming a scaffold for enzymes known as caspases to activate and immediately initiate cell death.
Science
[ Load more ]