fromThe Art Newspaper - International art news and events
1 week agoArt collective Cooking Sections' food projects are helping save the planet
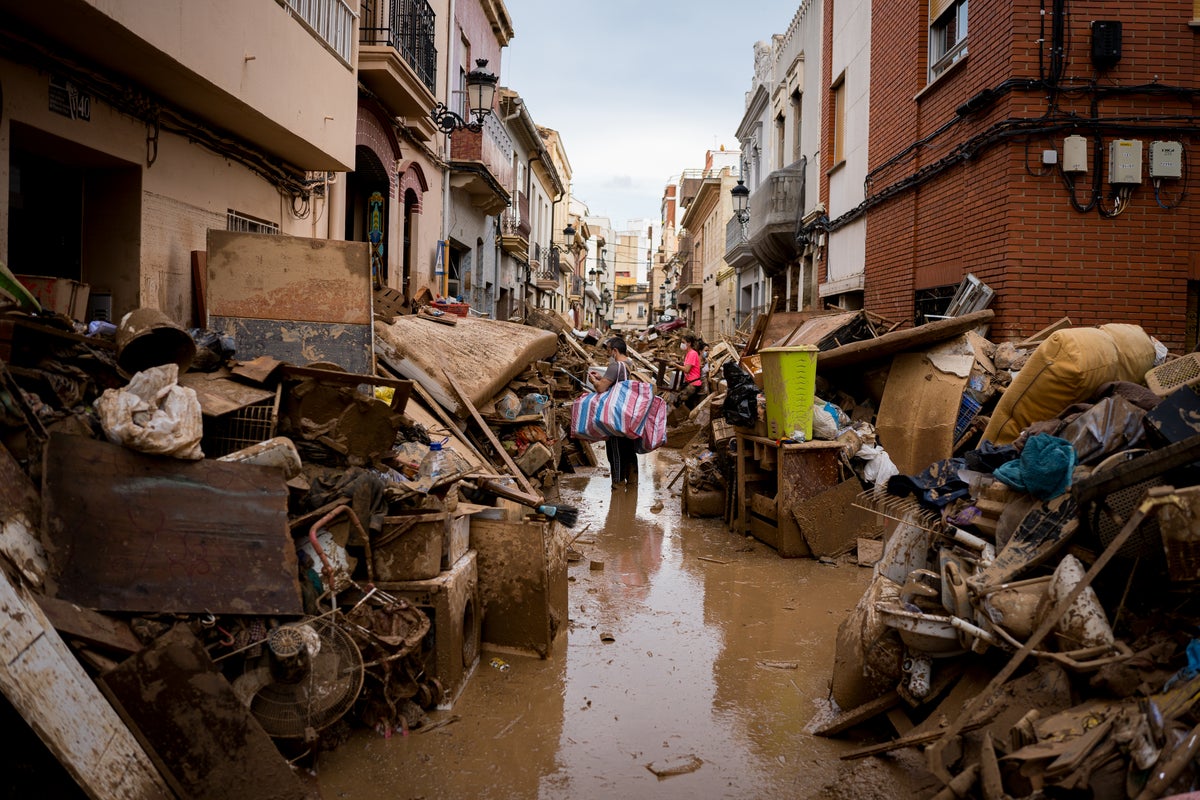
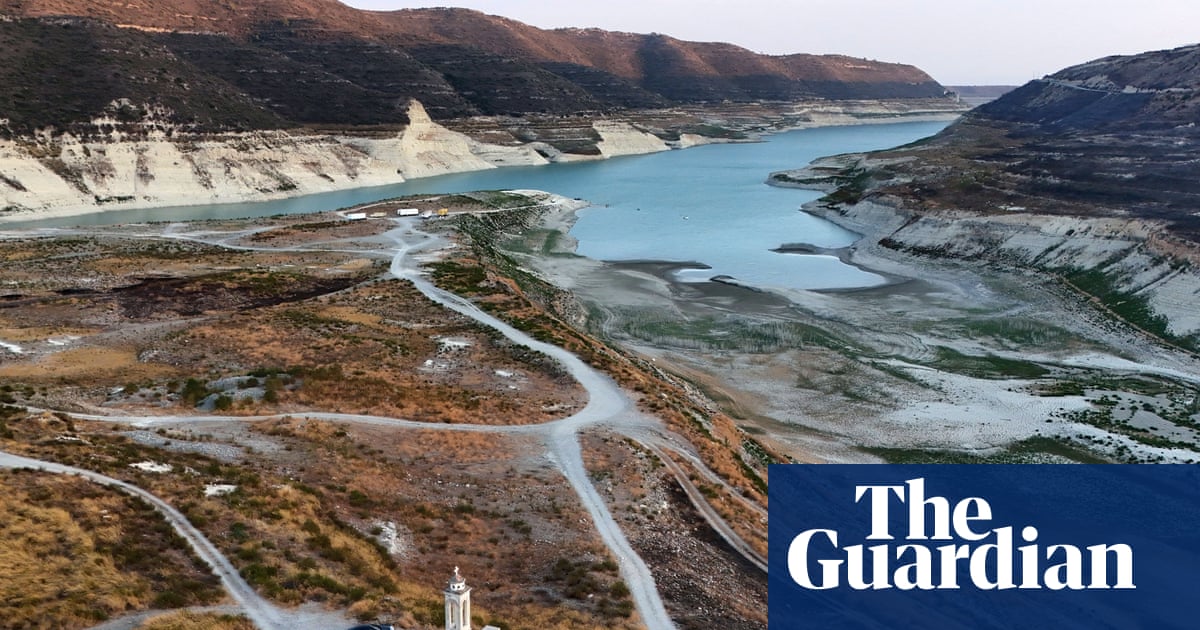
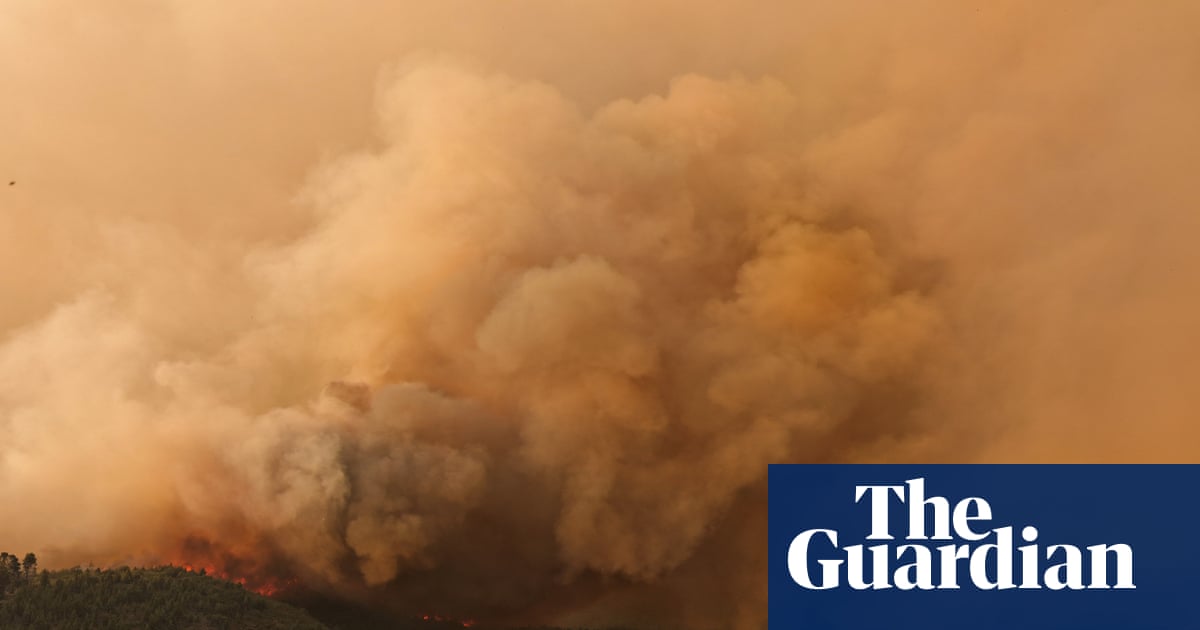
Since the duo got together as fellow students at Goldsmiths Centre for Research Architecture in 2013, they have been using the production and consumption of food as the focus for numerous long-term, site-specific projects that address how we should live-and eat in particular-in the face of climate change. As they put it: "Food is both deeply connected to the environment and to ecology but at the same time is also intersectional: every living organism on this planet is invested and preoccupied with processes of metabolism, ingestion and the acquisition of nutrients."