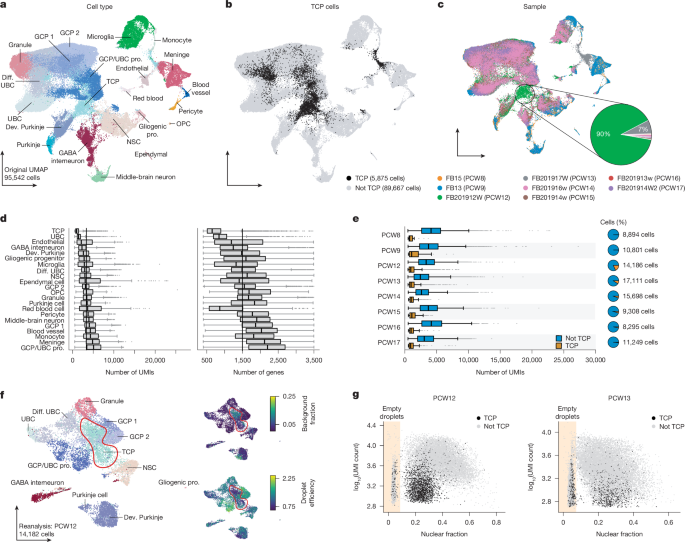
"The study focused on analyzing human fetal cerebellum to understand the cellular and molecular mechanisms driving neurogenesis and developmental pathways in pediatric brain tumors."
"In situ hybridization techniques revealed distinct patterns of gene expression that highlight critical developmental roles in glioblastoma and medulloblastoma formation."
"Computational analyses provided insights into the interactions between various cell types, elucidating how these dynamics contribute to tumor initiation and progression in the pediatric brain."
"A collaborative effort across institutions allowed for a multifaceted approach to studying brain tumor development, showcasing the importance of cross-disciplinary research in pediatric oncology."
The research investigated the cellular and molecular mechanisms of neurogenesis related to pediatric brain tumors by analyzing human fetal cerebellum samples. Distinct gene expression patterns were revealed through in situ hybridizations, implicating their role in the development of glioblastoma and medulloblastoma. The study employed advanced computational analyses to explore interactions among various cell types, contributing to understanding tumor initiation and progression. The work exemplifies the need for collaborative research efforts across multiple institutions to address complex challenges in pediatric oncology.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]