"The multifaceted nature of active galactic nuclei necessitates a comprehensive understanding of their roles within galaxy evolution, particularly through merging processes."
"Understanding the unified models of AGN and quasars is essential, as they form the backbone of contemporary astrophysical theories regarding supermassive black holes."
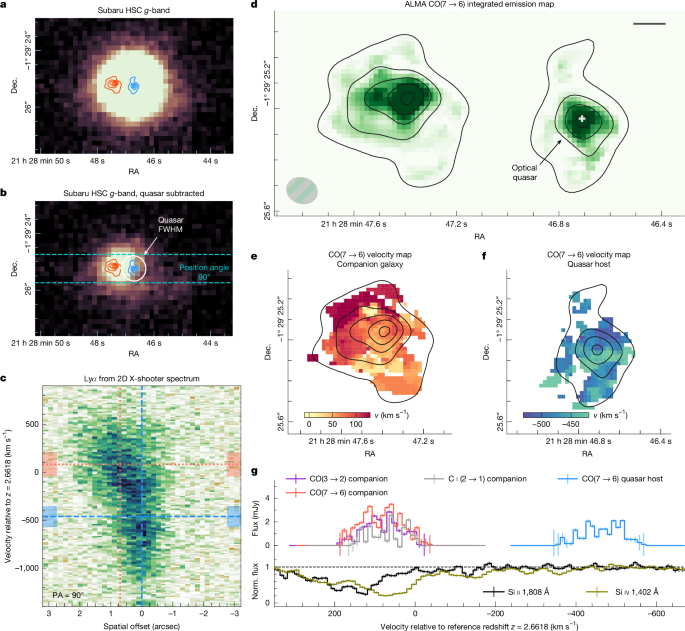
"Observations have highlighted that interactions between galaxies often trigger significant events, such as the activity within active galactic nuclei and the growth of black holes."
"The research discusses the importance of high-redshift quasars in illuminating the assembly and growth of supermassive black holes since the early universe."
This article explores the established unified models for active galactic nuclei (AGN) and quasars, emphasizing their significance in galaxy evolution. It reviews how interactions and mergers among galaxies catalyze AGN activity and contribute to the growth of supermassive black holes. Additionally, the article discusses observational evidence from various studies, including recent findings of high-redshift quasars, which provide insights into black hole formation in the early universe. The comprehensive assessment reflects not only on theoretical frameworks but also on empirical data supporting these models.
Read at www.nature.com
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]