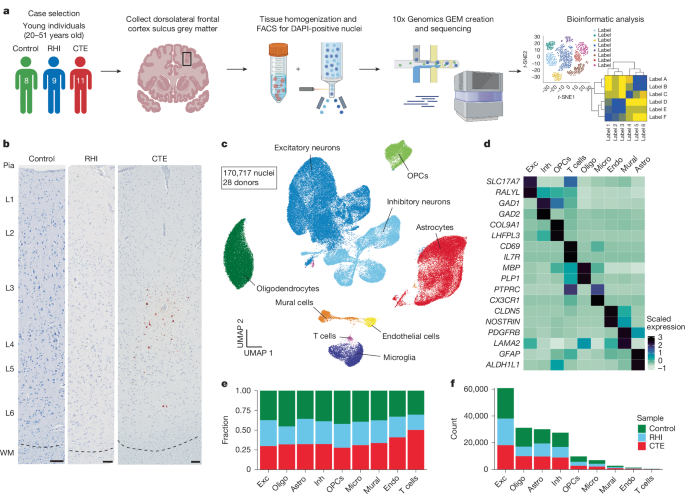
"Each year, millions of individuals are exposed to RHIs through contact sports, military service and domestic violence. These RHIs are often non-symptomatic and non-concussive, and can occur thousands of times per year, over the course of decades in some cases. CTE, a progressive tauopathy caused by exposure to RHI1,2, is observed in individuals as young as 17. Risk for CTE in exposed individuals is associated with the number of years of exposure to RHI and the cumulative force of the hits endured3,4."
"Currently, CTE can only be diagnosed post-mortem through identification of p-tau aggregates in neurons around blood vessels at the depth of the cortical sulcus. Our previous research suggests that microglia-mediated neuroinflammation occurs prior to the deposition of p-tau5. Other work has demonstrated that RHI exposure is associated with astrocytic activation, white matter inflammation and damage, blood-brain barrier (BBB) breakdown, serum protein leakage and increases in vascular density in the CTE brain5,6,7,8,9."
Millions of individuals are exposed to repetitive head impacts (RHI) through contact sports, military service and domestic violence, often in non-symptomatic and non-concussive forms that can occur thousands of times per year over decades. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a progressive tauopathy caused by RHI and can manifest in individuals as young as 17. Risk for CTE correlates with years of RHI exposure and cumulative impact force. CTE diagnosis currently requires post-mortem identification of perivascular p-tau aggregates at the cortical sulcus depth. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation, astrocytic activation, white matter inflammation, blood-brain barrier breakdown, serum protein leakage and increased vascular density are observed prior to overt neurodegeneration and likely drive early clinical impairments. Detailed characterization of early cellular changes is necessary to identify biomarkers and therapeutic targets for early disease stages.
#chronic-traumatic-encephalopathy #repetitive-head-impacts #neuroinflammation #blood-brain-barrier #astrocyte-activation
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]