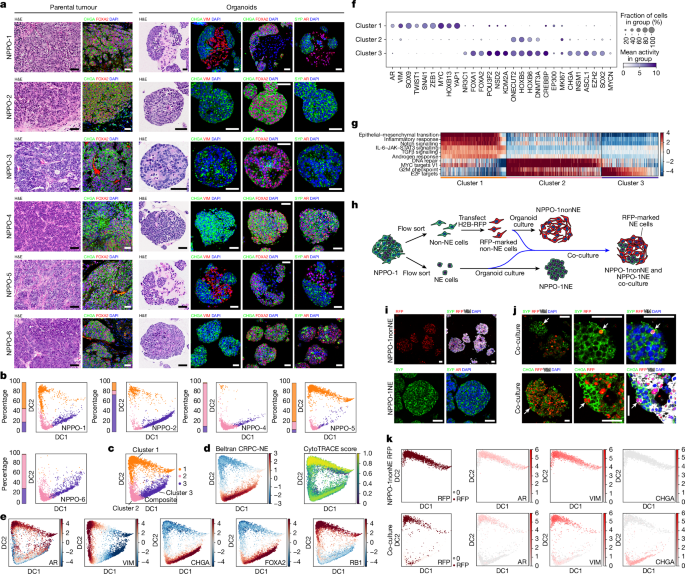
"Such CRPCs, typically in the metastatic setting (mCRPC), often retain adenocarcinoma histology and AR expression (CRPC-AR)3, but can also display other histological and molecular subtypes that are AR low or AR - and arise through lineage plasticity. Notably, progression to CRPC-NE occurs through a lineage switch, in which cells transdifferentiate from a luminal adenocarcinoma subtype to a neuroendocrine subtype that is highly resistant to AR inhibitors."
"CRPC-NE usually lacks AR expression and instead expresses neuroendocrine markers such as synaptophysin (SYP) and chromogranin A (CHGA)10. Moreover, the classical form of neuroendocrine prostate cancer that arises in primary tumours in the absence of androgen deprivation (de novo neuroendocrine prostate cancer) is rare (less than 0.1%)11, whereas CRPC-NE occurs in approximately 5-25% of mCRPC. CRPC-NE and other CRPC subtypes (for example, WNT-dependent CRPC (CRPC-WNT)) are characterized by their aggressiveness, treatment resistance and poor clinical outcomes."
"There is considerable evidence that lineage plasticity in CRPC is mediated by epigenetic reprogramming. Here we first describe mouse organoid models that recapitulate key features of human CRPC-NE and neuroendocrine transdifferentiation in culture. We show that neuroendocrine prostate tumour cells have increased levels of histone H3 lysine 36 dimethylation (H3K36me2), which is catalysed by NSD2 (also known as MMSET or WHSC1)15,16."
"Using both mouse and human patient-derived organoid models of CRPC-NE, we demonstrate that NSD2 is required for the maintenance of neuroendocrine differentiation and castration resistance. Finally, using a first-in-class small molecule, we demonstrate that pharmacological inhibition of NSD2 reverses"
Potent AR-pathway inhibitors initially control prostate cancer but resistance leads to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). CRPC can retain AR and adenocarcinoma features or undergo lineage plasticity to CRPC-NE, which lacks AR and expresses neuroendocrine markers such as SYP and CHGA. De novo neuroendocrine prostate cancer is rare, while CRPC-NE appears in approximately 5–25% of metastatic CRPC and is aggressive and treatment-resistant. Lineage plasticity is associated with epigenetic reprogramming. Mouse and patient-derived organoid models recapitulate CRPC-NE. Neuroendocrine tumour cells show increased H3K36me2 catalysed by NSD2, which is required for maintenance of neuroendocrine differentiation and castration resistance, and pharmacological NSD2 inhibition reverses neuroendocrine features in models.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]