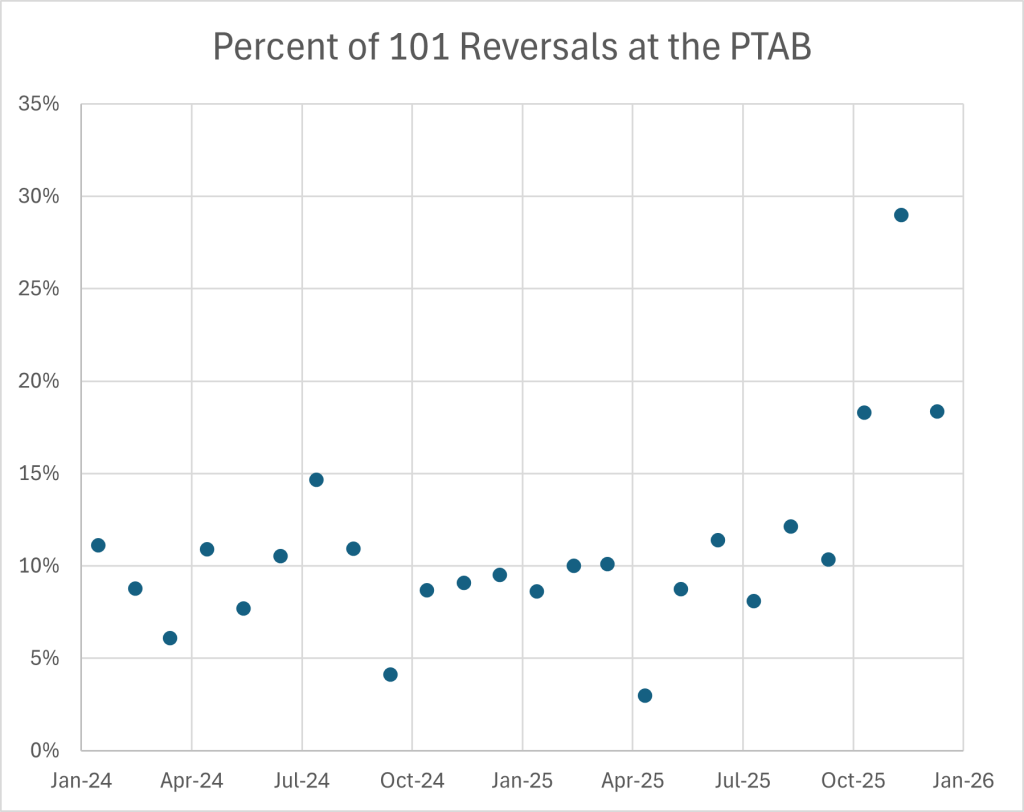
"The reversal rate, which hovered between 8% and 12% for most of 2024 and early 2025, jumped to 18% in October 2025 and spiked to 29% in November. A recent rehearing decision in Ex parte Mercer, Appeal 2024-002371 (PTAB Oct. 31, 2025), illustrates one aspect of the Board's new approach: demanding evidentiary support for findings that claimed elements are "well-understood, routine, conventional activity" under Alice step two."
"The chart above shows the percentage of Section 101 rejections reversed by the Board (without a new ground of rejection) in ex parte appeals, by month. As I discussed in October, the Board's Section 101 reversal rate began climbing shortly after Director Squires took office. Dennis Crouch, PTAB Responds to New Director with Increased § 101 Reversals, Patently-O (Oct. 2025). The trend has accelerated. The November 2025 reversal rate of 29% represents nearly a threefold increase from the rates that prevailed through most of 2024."
"The application claims methods for achieving synchronized execution across geographically dispersed servers. The core problem addressed is network latency: when a primary server needs multiple remote servers to act simultaneously, varying transmission delays mean messages arrive at different times. The claimed solution involves the primary server determining an execution time, packaging that time with each message as an instruction, transmitting those instructions to geographically dispersed secondary servers, and having each secondary server store the execution time and perform its action only when the local current time matches."
PTAB reversal rates for Section 101 rejections rose from roughly 8–12% through most of 2024 to 18% in October 2025 and 29% in November 2025. The Board is increasingly demanding evidentiary support for findings that claimed elements are "well-understood, routine, conventional activity" under Alice step two. Ex parte Mercer exemplifies that approach, involving claimed methods to synchronize execution across geographically dispersed servers to address network latency. The claimed solution has a primary server determine an execution time, include that time with each message, and have secondary servers store the time and act only when local time matches. The November rate marks nearly a threefold increase from 2024.
Read at Patently-O
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]