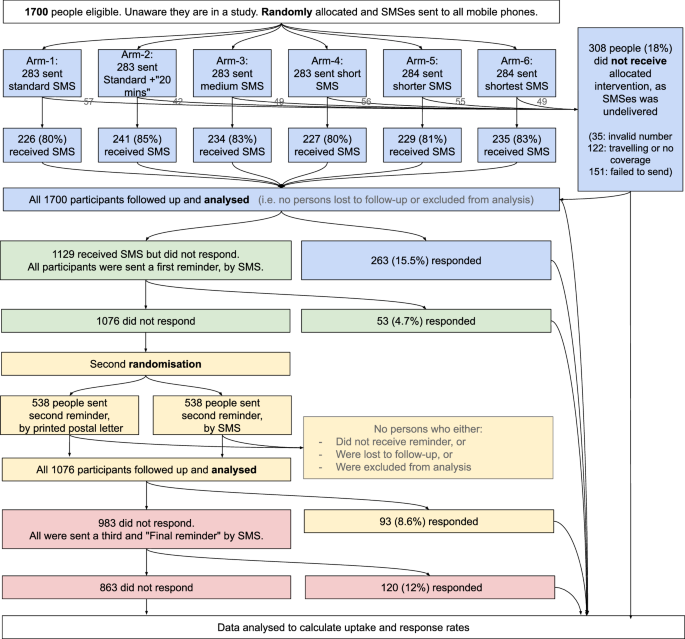
"A six-arm pragmatic unregistered randomised controlled trial (RCT) showed that uptake varied from 12% with standard SMS to 20% with the shortest SMS, a significant difference (P = 0.009)."
"Three sequential reminders were tested, with the first SMS reminder increasing uptake by +3%. The postal reminder proved to be more effective (+7%), while the final SMS reminder also contributed +7%."
"Incorporating digital care alongside in-person care could potentially raise overall uptake for screening from approximately 50% to 60%, presenting a viable strategy for improving engagement."
"Agile evaluations allow rapid improvements in invitation systems, demonstrating the importance of iterative feedback and adaptation in enhancing participation in health screening."
Digital screening interventions were tested among 1700 Londoners aged 40-74 without cardiovascular disease. A randomized controlled trial indicated varied uptake rates, which ranged from 12% to 20%. Various reminder methods were implemented; the postal reminder was notably more effective than SMS reminders. The combination of digital and in-person services may raise the overall screening uptake. Agile approaches facilitate ongoing improvements to invitation strategies. Findings support the potential of mixed-modality screening programs to enhance participation rates in health checks.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]