"We've witnessed remarkable progression: from ChatGPT's context-unaware snippets in 2022, to GitHub Copilot's editor integration in 2023, to autonomous coding agents like OpenHands in 2024 that could run code, debug errors, and iterate until completion. Now in 2025, we're entering the era of parallel agent orchestration - deploying fleets of AI agents to tackle large-scale refactoring projects that would otherwise take months to complete manually."
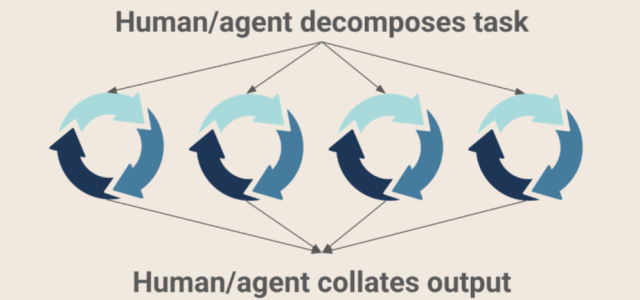
"The key insight is that massive refactors aren't actually single tasks - they're collections of smaller, automatable subtasks. The challenge lies in intelligent decomposition and coordination. Simply telling an agent "port this codebase to Go" results in incomplete solutions. Instead, we need to break these projects into bite-sized pieces that individual agents can handle autonomously. Piece by Piece: Move through your codebase systematically - directory by directory, file by file. This works well for incremental changes like adding type annotations to Python applications."
AI-powered development has progressed from isolated code snippets to integrated assistants and autonomous coding agents capable of running and debugging code. In 2025, orchestration of parallel agents enables fleets of AI to undertake large-scale refactors that previously took months. Massive refactors should be decomposed into automatable subtasks and coordinated intelligently rather than treated as single monolithic commands. Effective strategies include systematic file- or directory-wise migration, navigating dependency trees from leaves inward, and creating scaffolding or shims to allow partial, iterative migration. Proper task decomposition and coordination allow agents to work autonomously and in parallel to complete complex migrations.
Read at Medium
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]