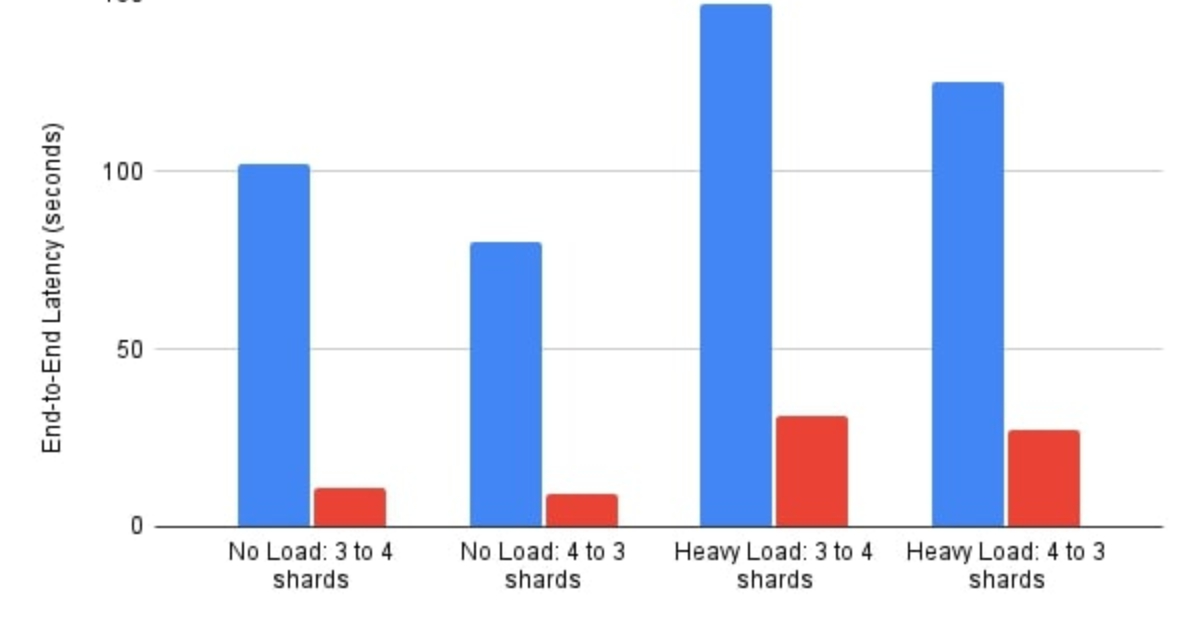
"The latest major version introduces atomic slot migrations, hash field expiration, and full support for numbered databases in cluster mode, enabling scaling to 2,000 nodes and achieving over 1 billion requests per second. Released one year after Valkey 8.0, Valkey 9.0 adds atomic slot migration, improving how clusters rebalance data. Unlike stepwise migrations that could change ownership mid-transfer, the new atomic movement is designed to ensure consistent key routing and predictable handoffs, reducing transient errors and simplifying live resharding."
"Previously, Valkey hashes could only expire as a whole, forcing users to split data across multiple keys when field-level expiration was needed. Valkey 9.0 allows individual hash fields to expire independently. In a separate article, Ran Shidlansik, senior software engineer at AWS, explains how hash field expiration works and why active, rather than lazy, expiration is used to reclaim expired hash fields. Shidlansik concludes: The benchmarks demonstrate that field-level expirations can be added to Valkey without compromising memory efficiency, or latency."
Valkey 9.0 introduces atomic slot migrations that move entire slots atomically between nodes to ensure consistent key routing and predictable handoffs. Keys are grouped into 16,384 slots and slot movement uses the AOF format, replacing stepwise key-by-key transfers and reducing transient errors during resharding. Hash field expiration now permits individual hash fields to expire independently, eliminating the need to split data across multiple keys and using active expiration to reclaim expired fields without harming memory efficiency or latency. Full numbered database support in cluster mode enables scaling to thousands of nodes and very high request throughput.
Read at InfoQ
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]