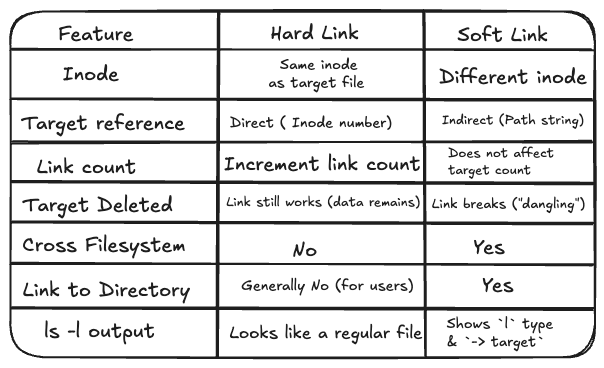
"A hard link is simply a new sticky note (a new filename) that points to the exact same ID card (the inode). When you create a hard link, you are creating a second directory entry that points directly to the same underlying inode as the original file. The original file and the hard link are not "original" and "shortcut" - they are peers."
"A soft link is a completely different (and new) file. It gets its own inode and its own data block. But instead of containing user data, the data block for a soft link contains just one simple piece of text: the path of the original file it's pointing to. When you access a soft link, the operating system reads its data, sees the path, and says, "Oh, you don't want me. You want this other file," and then it opens that file instead."
Hard links create additional directory entries that point to the same inode. Creating a hard link adds a second directory entry that references the same underlying inode as the original file. The original file and the hard link act as peers rather than original and shortcut, sharing the same data, permissions, and owner. Soft links are separate files with their own inode and data block. The data block of a soft link stores the path of the target file, and accessing the soft link causes the operating system to read that path and open the target file.
Read at Medium
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]