"Kalman filter-based Inertial Navigation System (INS) is a reliable and efficient method to estimate the position of a pedestrian indoors."
"The Quasi-static Magnetic field Detection (QMD) method is proposed to detect the pure magnetic field and then selects the EC or HDR algorithm accordingly."
"The Advanced IEZ (AIEZ) integrates QMD, EC, and HDR algorithms into the IEZ framework to provide an improved Pedestrian Dead Reckoning solution."
"In urban canyons or indoor environments, GNSS becomes unreliable due to signal attenuation, interference, and shade, prompting research into Local Positioning Systems."
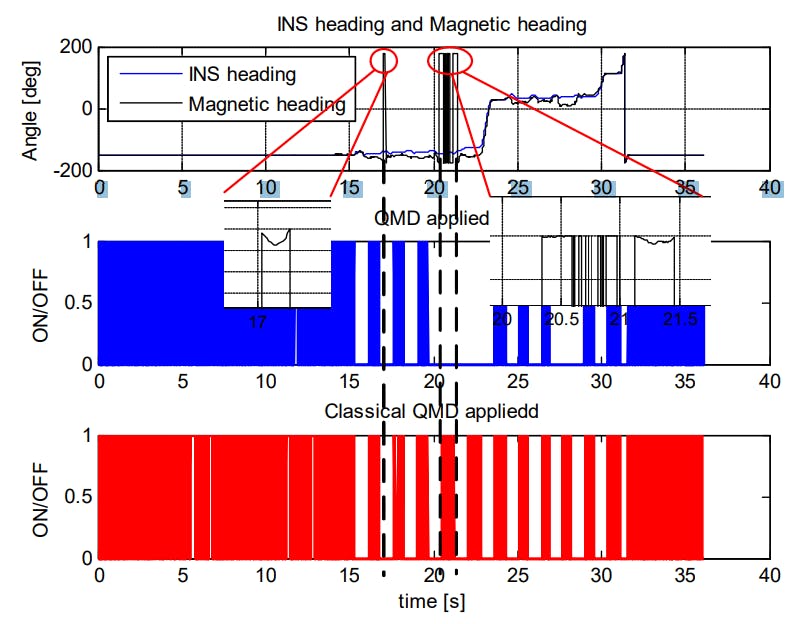
Kalman filter-based Inertial Navigation System (INS) is utilized for estimating the indoor position of pedestrians. It employs the IEZ methodology, which incorporates Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) and Zero velocity Updating (ZUPT). Heading errors pose significant challenges in these systems. To mitigate such errors, an Electronic Compass (EC) is introduced, although magnetic disturbances can negatively impact it. The proposed Quasi-static Magnetic field Detection (QMD) method detects pure magnetic fields and helps select the appropriate algorithm between EC and Heuristic heading Drift Reduction (HDR). This integration leads to the Advanced IEZ (AIEZ) solution for improved Pedestrian Dead Reckoning.
Read at Hackernoon
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]