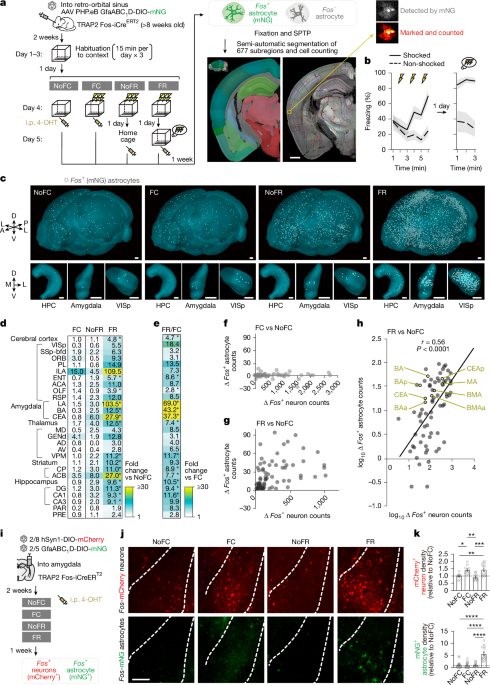
"Recall transiently destabilizes memories, which require re-stabilization to become long-lasting. Despite its importance in human cognition and neuropsychiatric disorders6,7, the mechanisms that specifically stabilize memories of critical experiences-those that are essential for survival and frequently marked by emotional salience and repetition-remain incompletely understood. Memory traces are linked to specialized neuronal ensembles (neuronal engrams), which include neuronal populations that become Fos+ during both initial and repeated experiences8."
"By tiling the entire mammalian central nervous system (CNS), astrocytes structurally and functionally interact with neurons and other glia. Their functions contribute to information processing and animal behaviour, and their dysfunctions are widely implicated in CNS disorders10,11. Astrocytes are known to be developmentally diverse and can adaptively change their molecular programmes in response to physiology11,15,16,17,18 and pathology-hereafter referred to as state-in specific ways that suggest flexibly altered functions in a context-dependent manner."
Memory recall transiently destabilizes stored information, requiring re-stabilization for long-term persistence. Critical experiences essential for survival and often emotionally salient and repeated require specialized stabilization mechanisms. Memory traces are embedded in neuronal engrams that include Fos+ neuronal populations active during initial and repeated experiences, but Fos expression alone is insufficient for stabilization, indicating additional cellular substrates. Astrocytes tile the central nervous system, structurally and functionally interacting with neurons and glia to support information processing and behaviour. Astrocytes are developmentally diverse and can adaptively alter molecular programmes in state-specific ways analogous to neuronal experience-dependent responses. Identifying how astrocyte subsets integrate inputs into behaviourally relevant astrocyte ensembles requires single-cell tools.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]