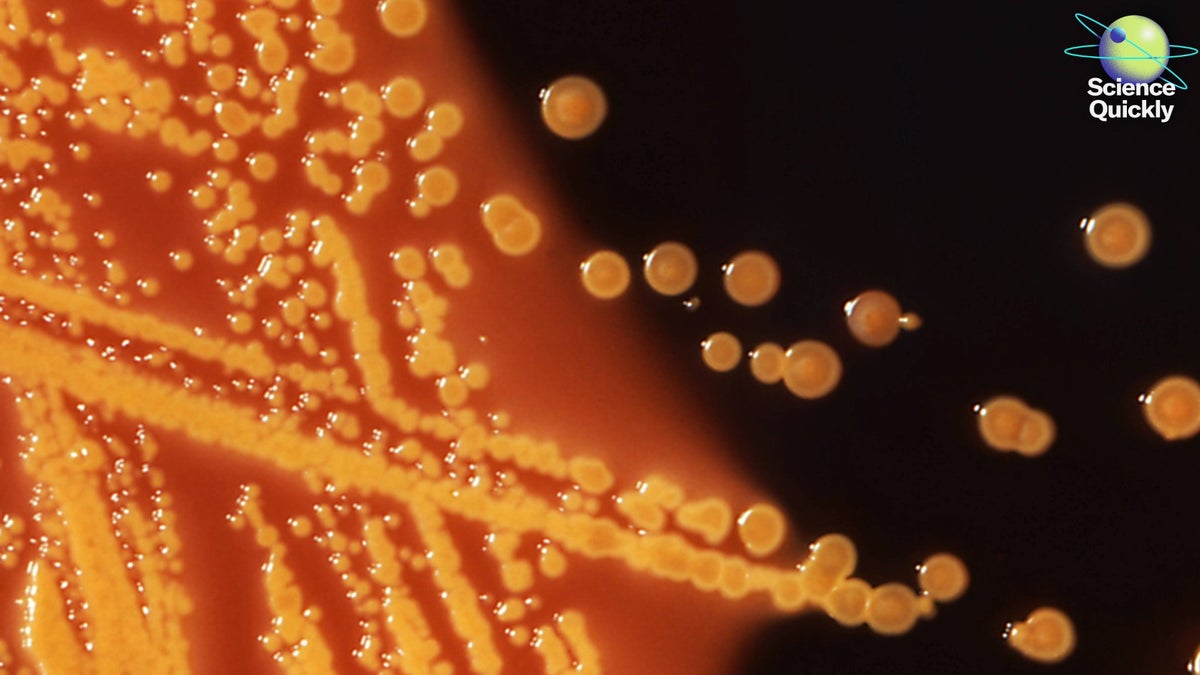
"Last Monday the World Health Organization warned that drug-resistant bacterial infections are on the rise around the globe. According to the WHO, superbugs that are antimicrobial-resistant, or AMR, contributed to almost five million deaths in 2019 and bore direct responsibility for more than one million. By 2023, one in six laboratory-confirmed bacterial infections showed resistance to antibiotics, with upwards of 40 percent of the medications commonly used in these cases having lost effectiveness over the five years prior."
"Low- and middle-income countries were more likely to be experiencing antibiotic resistance, according to the New York Times. And, in fact, the situation could be worse than it appears: the WHO noted that just 48 percent of countries actually shared data on antimicrobial resistance and of those roughly half had lacking tracking systems. Improving surveillance over the coming years will be crucial in the fight against superbugs, the agency said."
Antimicrobial-resistant bacterial infections are increasing worldwide, contributing to almost five million deaths in 2019 and directly causing over one million deaths. By 2023, one in six laboratory-confirmed bacterial infections showed antibiotic resistance, and roughly 40 percent of commonly used medications had lost effectiveness over the previous five years. Low- and middle-income countries face higher likelihoods of antibiotic resistance. Only 48 percent of countries reported antimicrobial resistance data, and about half of those reporters had inadequate tracking systems. Improving surveillance is crucial to control superbugs. New York confirmed a locally acquired chikungunya case on Long Island, linked to travel within the county but not internationally. Chikungunya is transmitted by two mosquito species, one present on Long Island.
Read at www.scientificamerican.com
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]