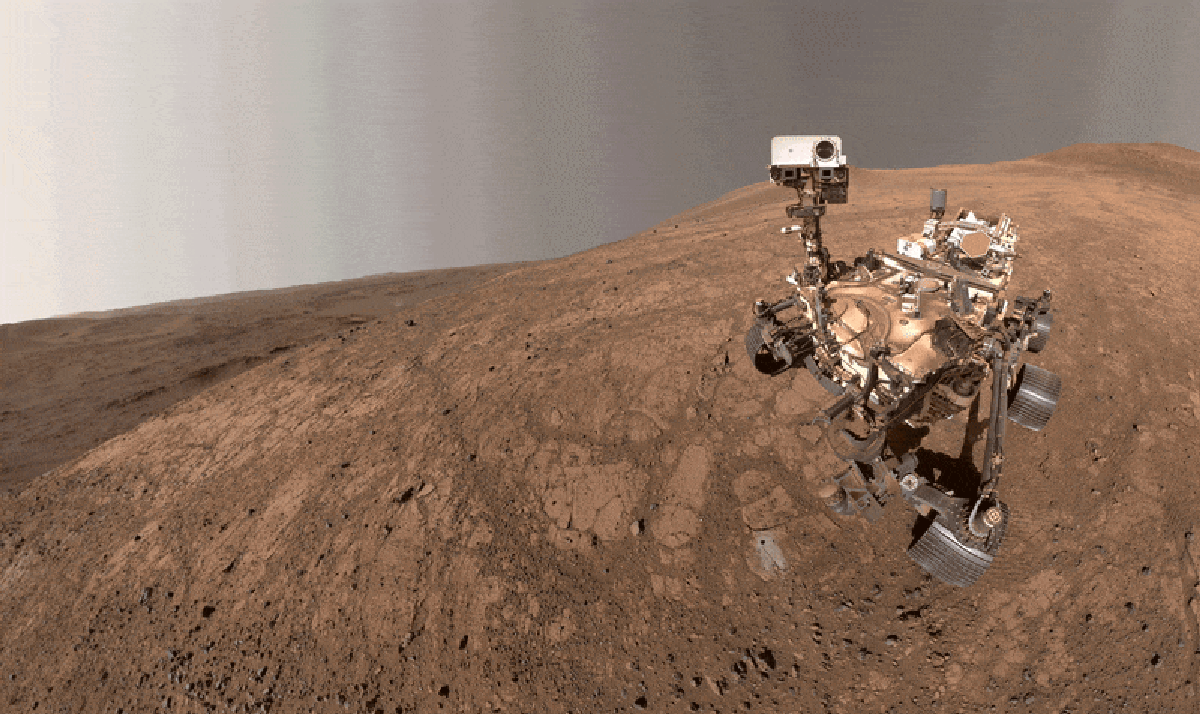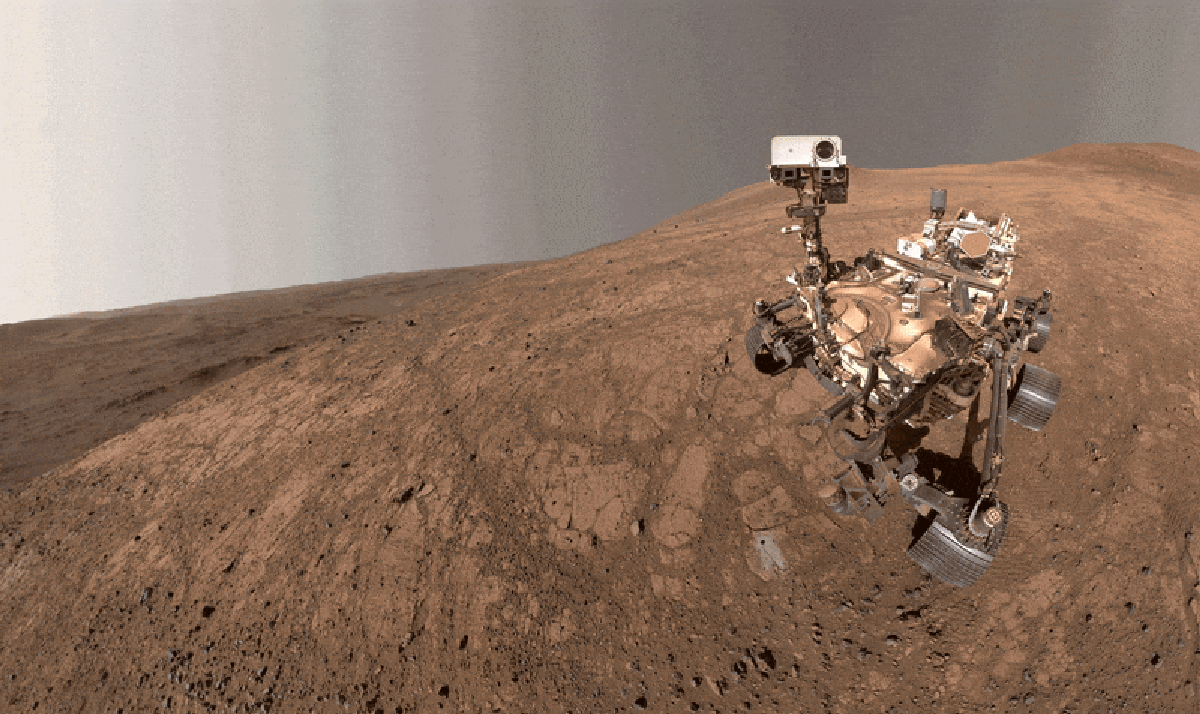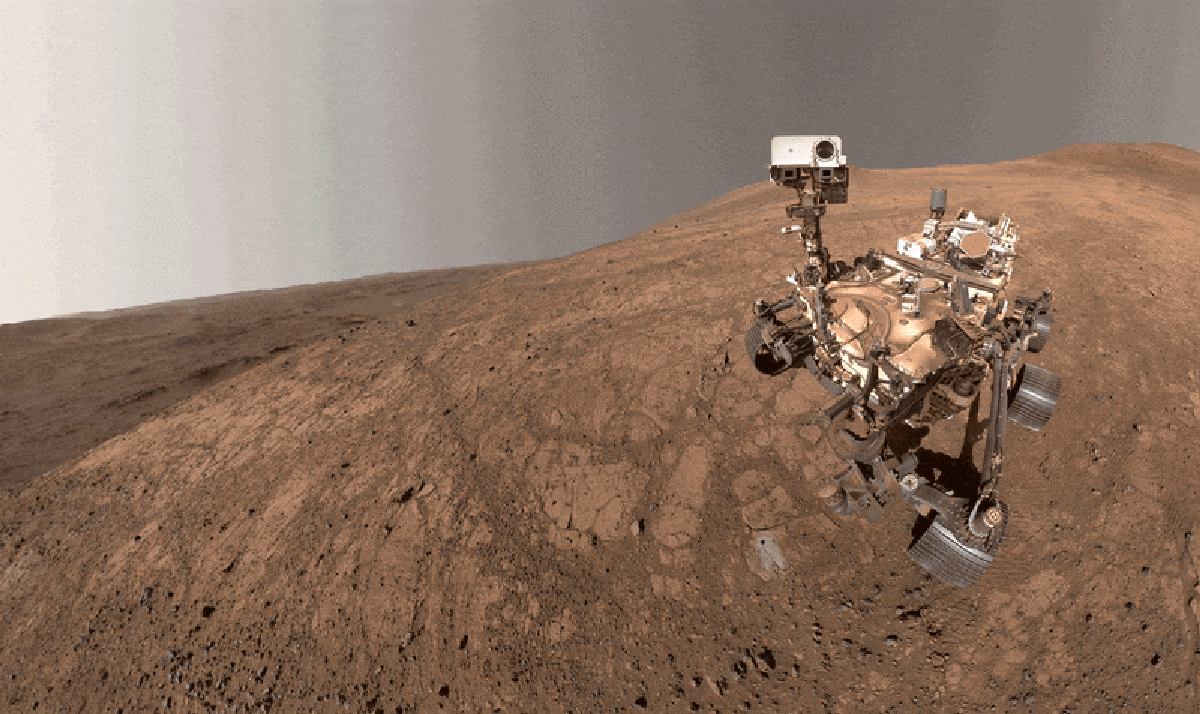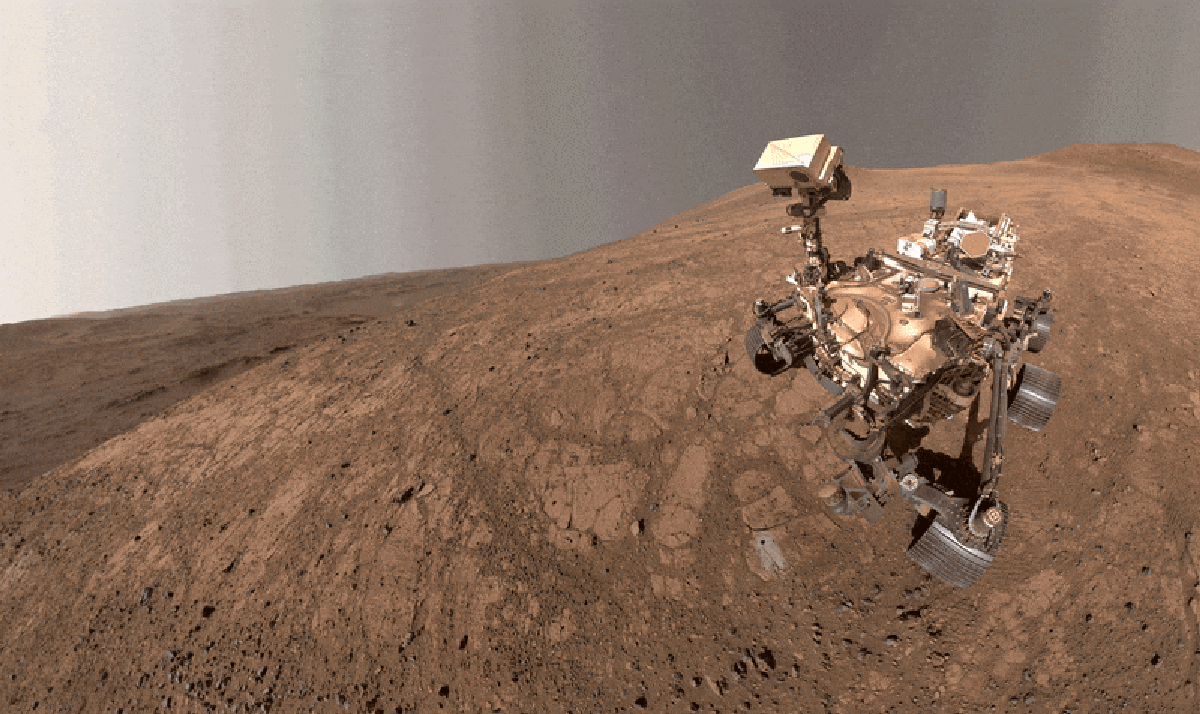
"Dubbed Cheyava Falls, the mudstone stood out to the researchers because its surface was spangled with strange speckles and ring-shaped blobs, which they referred to as poppy seeds and leopard spots. They also discovered that it was packed with organic matterchemical compounds of carbon, the elemental cornerstone of biology as we know it. Organic-rich rocks right here on Earth sometimes contain similar features, which tend to be created by microbial life."
"To know for sure whether Cheyava Falls is proof of past life on Marsor instead just a weird quirk of lifeless organic chemistryastrobiologists want to bring some of the rock back to Earth for closer study. But the NASA-led international program to do just that, known as Mars Sample Return (MSR), is in political limbo, beset by ballooning costs and flagging federal support."
Cheyava Falls is a school-desk-sized mudstone on Mars formed from fine, water-washed sediments on the floor of a long-lost lake about 3.5 billion years ago in Jezero Crater. The rock's surface shows speckles and ring-shaped blobs nicknamed poppy seeds and leopard spots and contains abundant organic matter, carbon-based compounds central to life. Similar features in Earth's organic-rich rocks are often microbial in origin. Perseverance observations led researchers to consider ancient microbes a plausible explanation for the spots and seeds. Determining a biological origin requires Earth laboratory study, but the Mars Sample Return program faces political, cost, and schedule challenges delaying sample return beyond 2040, prompting NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory to pursue an alternate plan B.
Read at www.scientificamerican.com
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]