"The human protease caspase-4 and its mouse orthologue caspase-11 defend against gram-negative bacteria3,4. Activated by bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the cytoplasm5,6,7, caspase-4 and caspase-11 cleave and activate the pore-forming protein gasdermin D (GSDMD) to cause a lytic form of cell death called pyroptosis8,9. Eliminating infected cells in this manner denies microorganisms their replicative niche. Other bacterial components, including toxins and DNA, are sensed by intracellular inflammasome complexes that activate caspase-1, which also induces pyroptosis by cleaving GSDMD1."
"Pathogenic bacteria have evolved to thwart host defence mechanisms. For example, the intestinal pathogen Shigella evades pyroptosis in human cells because its ubiquitin ligase IpaH7.8 targets GSDMD and GSDMB for proteasomal degradation10,11,12. Granzyme A cleaves GSDMB to elicit pyroptosis when infected cells are targeted by cytotoxic lymphocytes13. Another Shigella effector, OspC3, suppresses pyroptosis by inhibiting caspase-4 and caspase-11 (refs. 14,15). Effectors from other pathogenic bacteria, including Yersinia YopM and E. coli NleA, suppress pyroptosis by inhibiting the activation of caspase-1 (refs. 16,17,18). E. coli NleF suppresses pyroptotic and apoptotic host cell death by inhibiting caspases 4, 8 and 9 (ref. 19)."
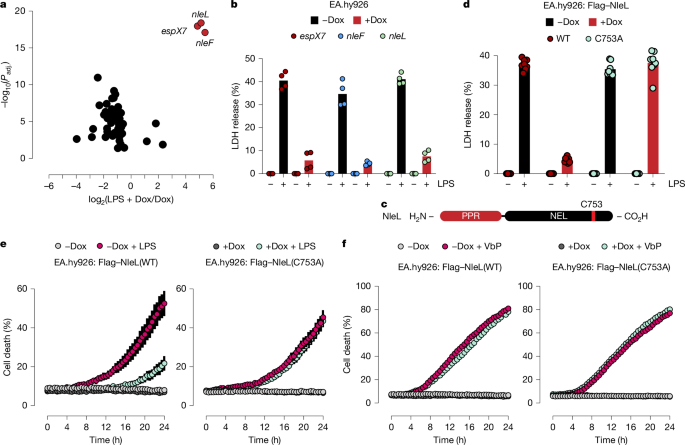
Caspase-4 and caspase-11 are activated by cytosolic LPS and cleave gasdermin D to induce lytic pyroptosis, eliminating infected cells. Inflammasome detection of other bacterial components activates caspase-1, which also cleaves gasdermin D to induce pyroptosis. Pathogenic bacteria produce effectors that block pyroptosis: Shigella IpaH7.8 targets GSDMD and GSDMB for proteasomal degradation; granzyme A cleaves GSDMB to trigger pyroptosis during cytotoxic lymphocyte attack; Shigella OspC3 inhibits caspase-4 and caspase-11. Yersinia YopM and E. coli NleA inhibit caspase-1 activation, and E. coli NleF inhibits caspases 4, 8 and 9. A pooled screen of 63 E. coli effectors identified NleL and NleF as protective against LPS-induced pyroptosis, with NleL expression improving survival and reducing LDH release in EA.hy926 cells.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]