"The understanding of this relationship has sparked inquiries across vast fields of biology and biological engineering as we read, edit and write the genetic information of organisms. Great advancements have been made toward these pursuits, from revolutions in DNA reading through long-read sequencing and the ability to generate terabytes of data from a single run1, to the breakthroughs in DNA editing with the major advancements in CRISPR-Cas technologies over the past decade2."
"De novo construction of DNA relies on synthetic single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) oligos as an input produced either through phosphoramidite synthesis12 or enzymatically using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)13. Owing to the cyclical nature of the synthesis process and the limited coupling efficiency at each step, the accuracy and yield of synthesized oligos decreases exponentially with increasing length3. Consequently, de novo production of DNA larger than just a few hundred bases requires accurate DNA assembly of these short oligos together in the correct order."
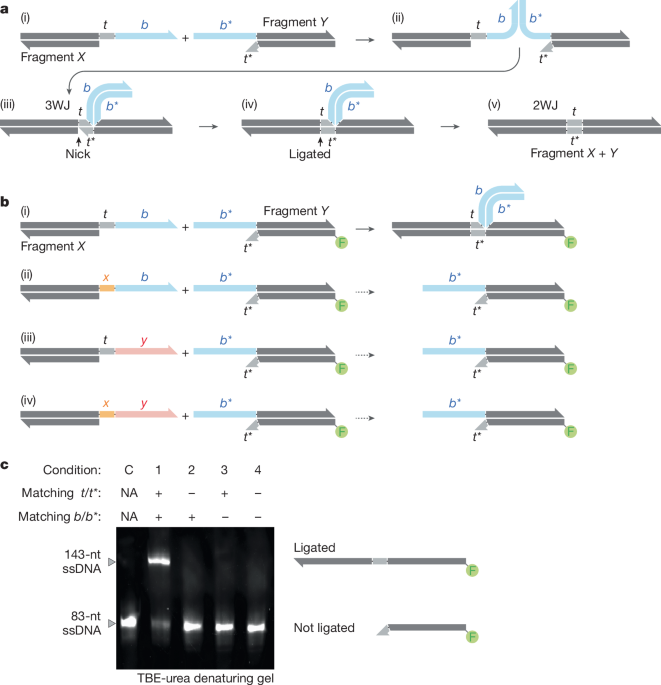
DNA encodes information enabling diverse biological functions and engineering applications. Advances in DNA reading with long-read sequencing and in DNA editing with CRISPR-Cas technologies have accelerated capabilities. De novo DNA construction depends on synthetic single-stranded DNA oligos produced by phosphoramidite chemistry or enzymatic TdT methods. The cyclical synthesis process and limited coupling efficiency reduce oligo accuracy and yield exponentially as length increases. Oligo synthesis length limits necessitate assembly of short fragments to build sequences larger than a few hundred bases. All existing assembly approaches rely on native two-way junctions between complementary single-stranded overhangs, constraining scalability and complexity.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]