"Quantum theory classifies particles into bosons and fermions based on the phase θ of their wavefunction upon exchange, affecting their collective behavior in significant ways."
"In two dimensions, anyons emerge as quasiparticles in topological states of matter, exhibiting fractional quantum statistics and showing behavior between bosons and fermions."
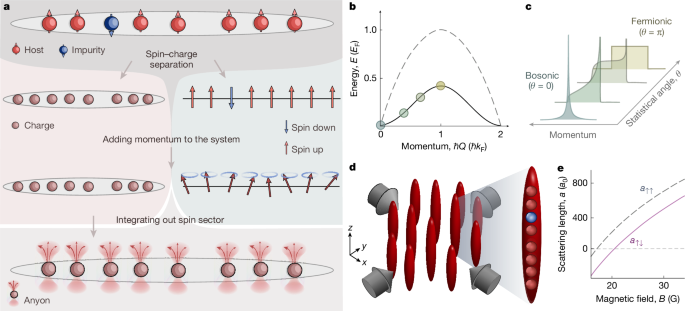
Quantum theory differentiates particles as bosons or fermions based on the phase θ of their wavefunction during exchanges, crucial for phenomena like elemental stability and superfluidity. In lower dimensions, anyons emerge, allowing for fractional quantum statistics. Existing as quasiparticles in topological matter, especially in 2D, anyons exhibit behaviors between bosons and fermions, impacting theoretical frameworks. The introduction of 1D anyons has opened discussions on unusual behaviors, including phase transitions and fractional Mott insulators, expanding the understanding of quantum systems.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]