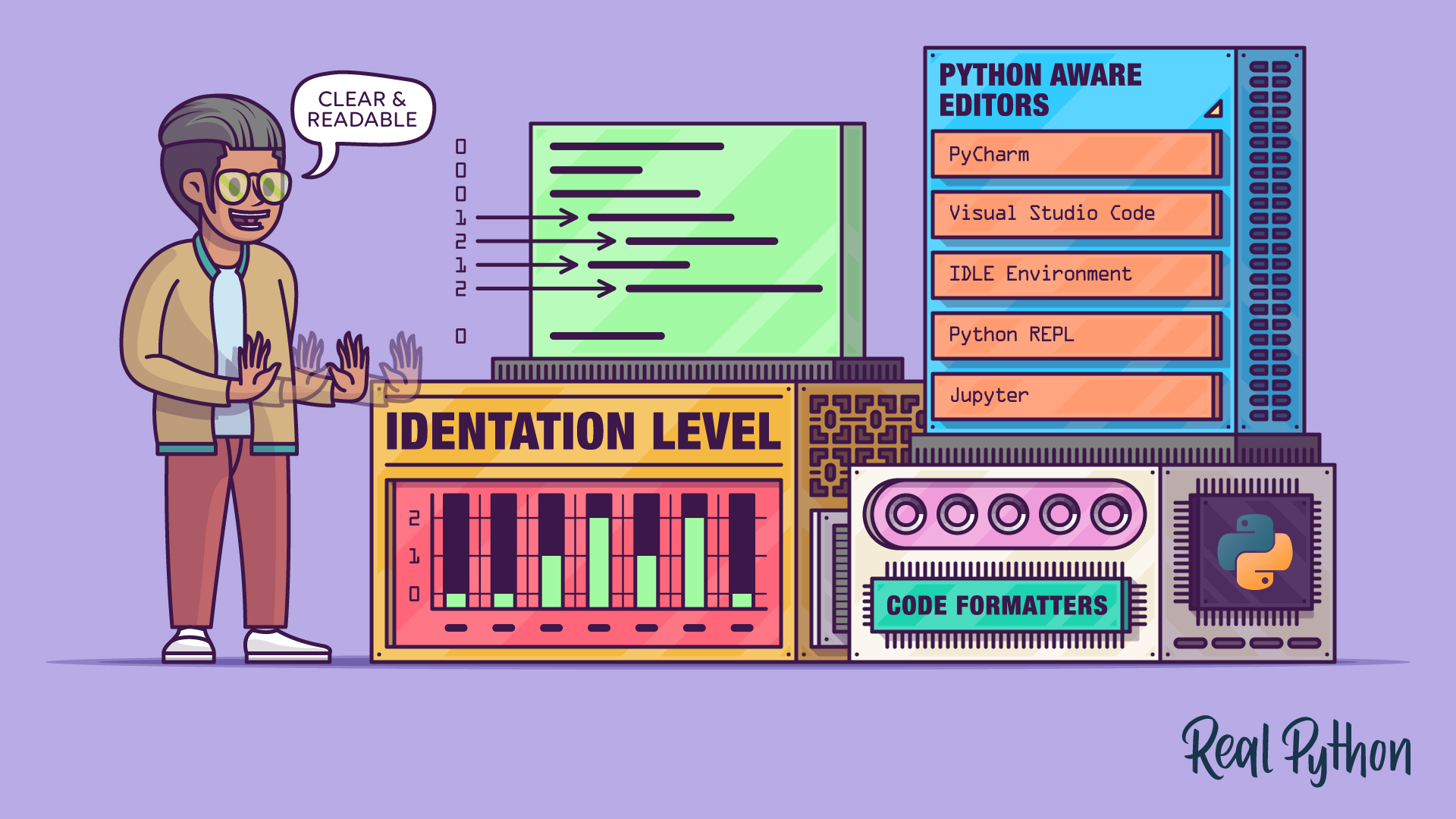
"Most editors and integrated development environments (IDEs) can indent Python code correctly with little to no input from the user. You'll see examples of this in the sections that follow. Python-Aware Editors In most cases, you'll be working in a Python-aware environment. This might be a full Python IDE such as PyCharm, a code editor like Visual Studio Code, the Python REPL, IPython, IDLE, or even a Jupyter notebook. All these environments understand Python syntax and indent your code properly as you type."
"Here's a small example to show this automatic indentation. You'll use the following code to see how each environment automatically indents as you type: This example shows how indenting happens automatically and how to de-indent a line of code. De-indenting-also called dedenting-means removing spaces at the beginning of a line, which moves the start of the line to the left."
Indentation in Python means adding spaces to the start of a line to shift it right and define code blocks. Most Python-aware editors and IDEs automatically indent and de-indent code as the user types. PEP 8 recommends using four spaces per indentation level and most environments follow that standard. De-indenting (dedenting) removes leading spaces to close code blocks and return to an outer indentation level. Each line belongs to a specific indentation level, and consecutive statements at the same level form a single group or code block. Proper indentation ensures correct program structure and readability.
Read at Realpython
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]