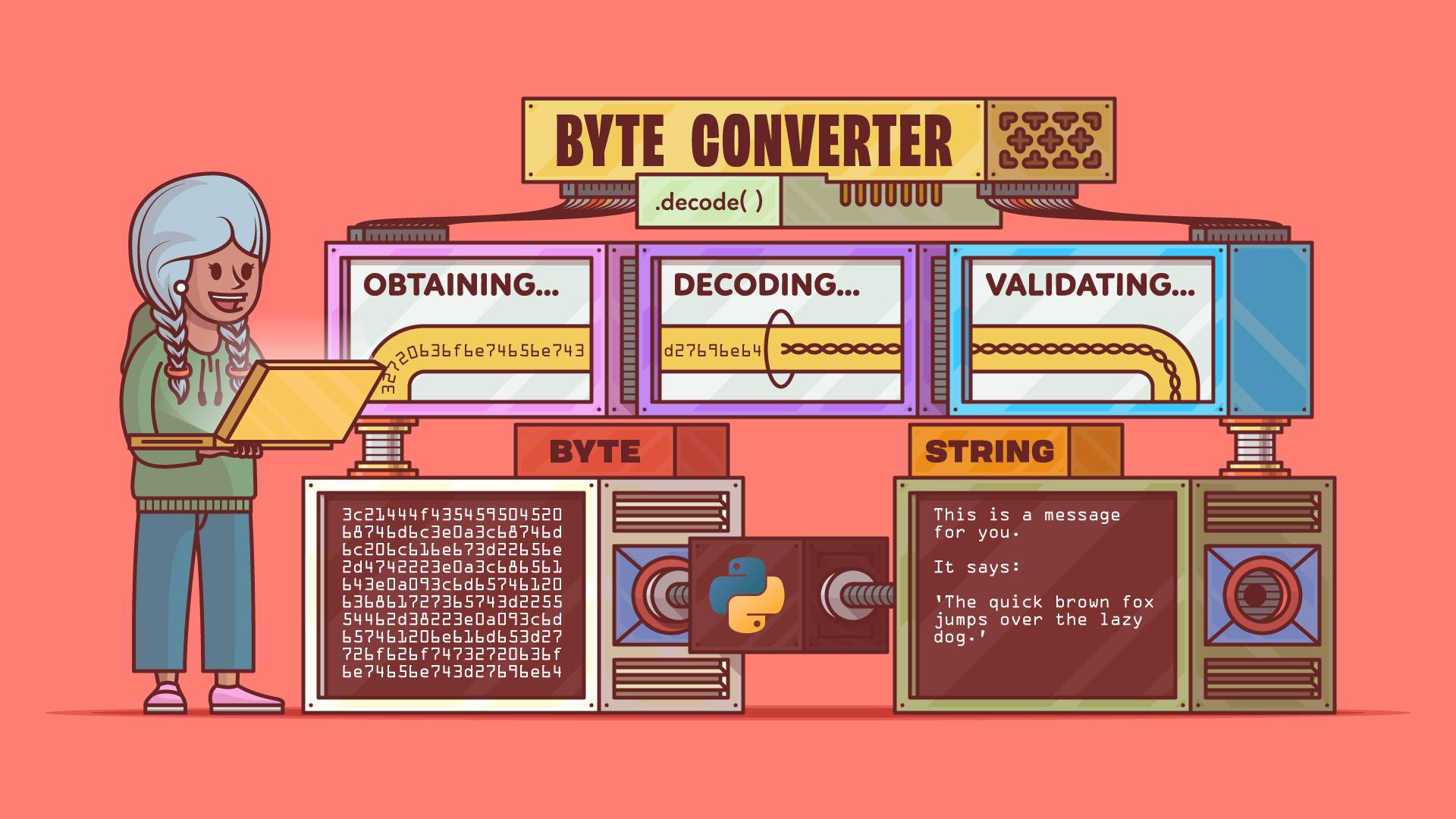
"Converting bytes into readable strings in Python is an effective way to work with raw bytes fetched from files, databases, or APIs. You can do this in just three steps using the bytes.decode() method. This guide lets you convert byte data into clean text, giving you a result similar to what's shown in the following example: By interpreting the bytes according to a specific character encoding, Python transforms numeric byte values into their corresponding characters."
"A byte is a fundamental unit of digital storage and processing. Composed of eight bits (binary digits), it's a basic building block of data in computing. Bytes represent a vast range of data types and are used extensively in data storage and in networking. It's important to be able to manage and handle bytes where they come up. Sometimes they need to be converted into strings for further use or comprehensibility."
Bytes are eight-bit units that form the basic building blocks of digital data, used in storage, networking, and computing. Python converts bytes to readable text by interpreting numeric byte values according to a chosen character encoding. The bytes.decode() method performs this conversion and yields normal strings suitable for processing. Common sources of byte data include files, databases, APIs, raw binary streams, Base64, hexadecimal strings, and network responses. Bytes can be created manually in code by prefixing a string literal with b, or retrieved using libraries such as urllib when accessing online resources.
Read at Realpython
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]