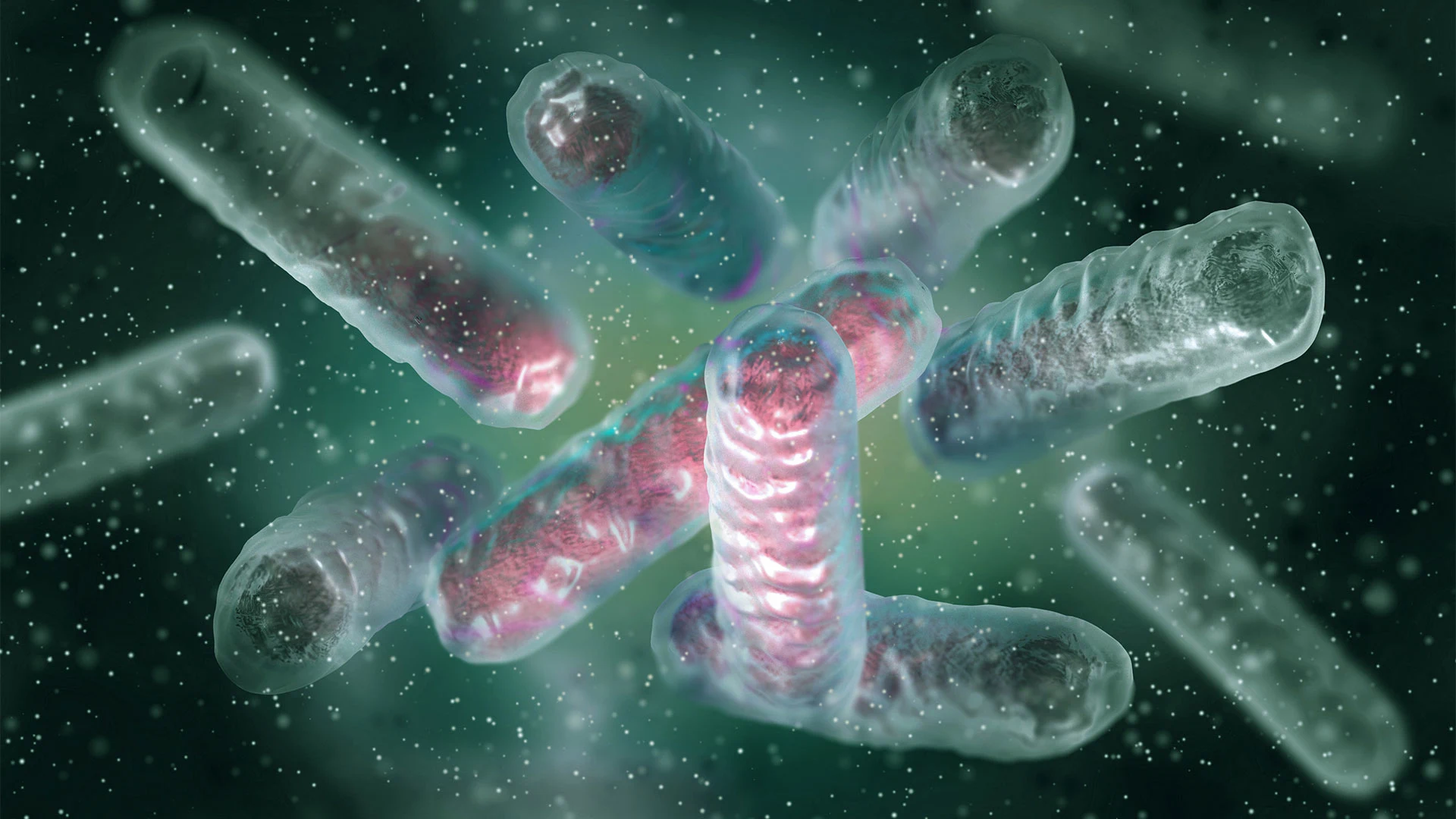
"The study, published on September 22 in the Annals of Internal Medicine, examines a bacteria called NDM-producing carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (NDM-CRE). Researchers found that, between 2019 and 2023, NDM-CRE infections surged by more than 460% in the U.S. These infections, which range from pneumonia to bloodstream and urinary tract infections, are extremely hard to treat and can be deadly due to their antibiotic-resistant properties-hence the name "superbug.""
"According to a January article from the CDC, antimicrobial resistance develops when drugs-like antibiotics and antifungals-pressure bacteria and fungi to adapt. These germs then develop resistance mechanisms in order to survive. Alarmingly, the CDC adds, "antimicrobial-resistant germs can share their resistance mechanisms with other germs that have not been exposed to antibiotics or antifungals." Essentially, "nightmare bacteria" lead to infections that are very difficult for doctors to treat."
"A " superbug " is a colloquial term for a strain of bacteria that has developed resistance to the drugs that were once able to kill it, particularly one that is spreading at a concerning rate."
NDM-producing carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (NDM-CRE) infections increased by more than 460% in the U.S. between 2019 and 2023. These infections cause pneumonia, bloodstream infections, and urinary tract infections and are extremely difficult to treat because of resistance to many antibiotics. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) were responsible for an estimated 12,700 infections and 1,100 deaths in 2020. NDM indicates the New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase enzyme, which confers resistance to nearly all available antibiotics. Antimicrobial resistance develops when antibiotics or antifungals pressure microbes to adapt, and resistant germs can share resistance mechanisms with other microbes.
Read at Fast Company
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]