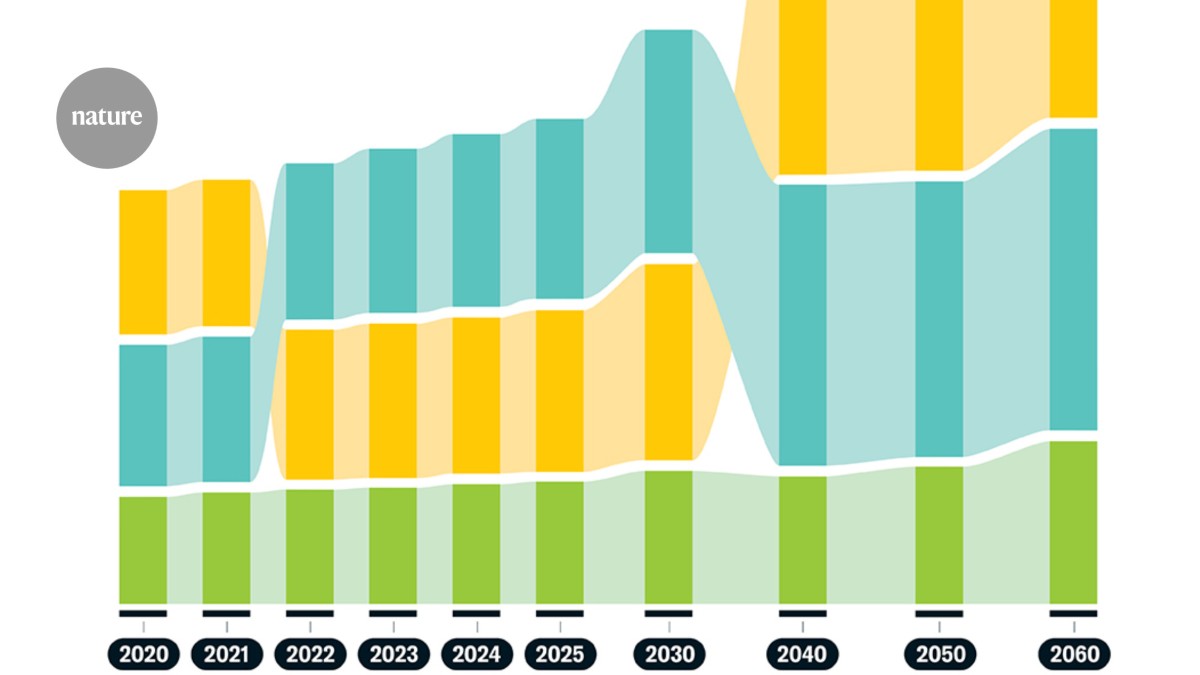
"The rate of Alzheimer's diagnosis has declined steadily in recent decades, but as baby boomers age, the number of new cases continues to rise. The top risk factor for dementia is age, and by 2030 more than one in five Americans will be 65 or older. That means the prevalence of Alzheimer's in the U.S. could exceed 13.8 million people by 2060."
"estimates that more than 770 nursing homes have closed in the U.S. since 2020, and recent federal cuts to Medicare and Medicaid will almost certainly decrease access to long-term care. Older adults overwhelmingly prefer to age in place and receive care at home, but for that to be possible, there must be support for home caregivers, enough people willing to do those jobs, and coordination between local and state services."
"A recently launched national resource funded by the National Institute on Aging, the State Alzheimer's Research Support Center (StARS), aims to help make all that a reality. By gathering data on the effectiveness, accessibility, and equity of state and regional programs for dementia care, then sharing those data, the researchers involved in the project hope to help states build partnerships that will aid policymakers at all levels in identifying the best solutions."
Alzheimer's diagnosis rates per capita have declined, but total cases increase as baby boomers age. Age is the main dementia risk, and by 2030 more than one in five Americans will be 65 or older. Alzheimer's prevalence could exceed 13.8 million people by 2060. Long-term-care capacity is shrinking: over 770 nursing homes closed since 2020, and federal cuts to Medicare and Medicaid may reduce access. Most older adults prefer home care, which requires caregiver support, an adequate workforce, and coordination across local and state services. The State Alzheimer's Research Support Center (StARS) will collect and share data on program effectiveness, accessibility, and equity to guide partnerships and policy.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]