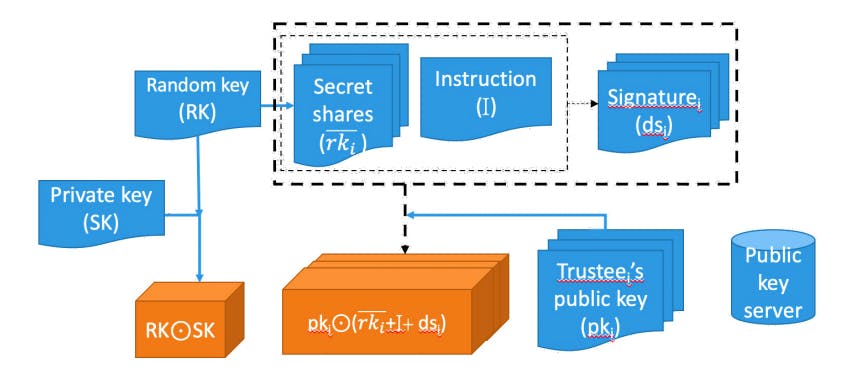
"The main weakness of the Direct-Escrow method is the possibility of collusion among trustees, which can compromise the owner's secret key. Despite improvements over traditional methods, vulnerabilities still exist that need addressing."
"In our proposed algorithms, we introduce both indirect-escrow and indirect-permission methods designed to minimize the risk of collusion while ensuring high security and reliability, though some weaknesses remain."
The article discusses various secret backup approaches, comparing traditional and alternative authenticator methods. While the Direct-Escrow method improves security, it remains susceptible to collusive attacks among trustees. The authors propose two new methods: indirect-escrow and indirect-permission, which aim to further mitigate collusion risks. Though the indirect methods show an increase in security and reliability, they also present a potential weakness when trustees can access secret shares during recovery, emphasizing the need for continued improvement in security measures against collusion.
Read at Hackernoon
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]