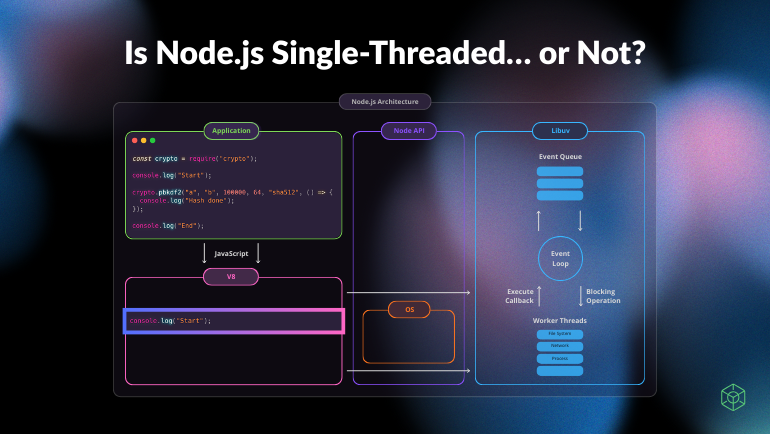
"You've probably heard: "Node.js is single-threaded." That statement is only partially correct. The JavaScript engine (V8) is single-threaded. Node.js as a runtime is not. Under the hood, Node.js uses multiple threads - through libuv and the operating system - to handle I/O and computationally expensive work. So the real question isn't whether Node.js is single-threaded. It's: Which part of Node.js are we talking about? Let's break this down using two concrete examples and a precise mental model of what actually happens inside the runtime."
"When we say something is single-threaded, we usually mean: There is one main call stack. Only one piece of JavaScript executes at a time on that thread. The main execution context does not run multiple JavaScript functions in parallel. In Node.js, that part is true - by default. The JavaScript execution environment (V8) contains: V8 ├─ Call Stack ├─ Heap └─ Microtask Queue There is exactly one main call stack responsible for executing JavaScript. However, this does not mean JavaScript can never run in parallel. Node.js allows parallel execution when you explicitly use mechanisms like Worker Threads or separate processes. But unless you opt into those models, JavaScript runs on a single main thread."
"What Happens Internally? Step 1 - console.log("Start") Executes immediately inside V8. Call stack: [ console.log("Start") ] Output: Pure synchronous execution on the main thread. Step 2 - setTimeout(...) V8 encounters setTimeout and delegates the timer registration: V8 ↓ Node.js bindings (C++) ↓ libuv libuv: Registers the timer in its internal timer data structure. Stores the callback. Returns control"
V8 runs JavaScript on a single main thread with one call stack, a heap, and a microtask queue. Node.js runtime includes libuv and native bindings that use additional threads and the operating system to handle timers, I/O, and computationally expensive work. setTimeout delegates timer registration to Node.js bindings and libuv, which registers timers and stores callbacks outside the V8 call stack. JavaScript callbacks return to the single V8 thread for execution. Parallel JavaScript execution is possible only when explicitly using Worker Threads or separate processes; otherwise JavaScript runs on the single main thread.
Read at The NodeSource Blog - Node.js Tutorials, Guides, and Updates
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]