"The study found that shorter SMS invitations and multi-modal reminders effectively increased participation rates in digital health checks, with email reminders proving most effective."
"Agile evaluations enable rapid improvements in invitation systems for health checks, showing that flexibility in approach can significantly enhance screening uptake."
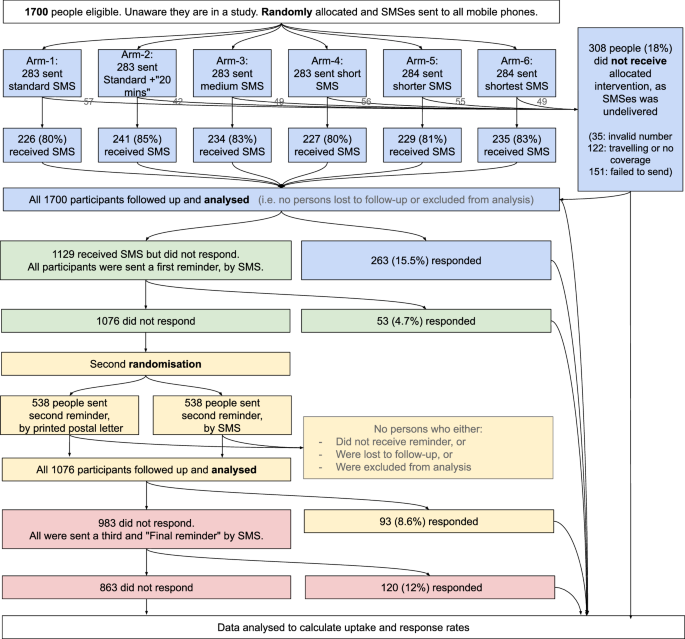
This research explored how digital health checks can be optimized for better uptake, specifically among Londoners aged 40-74 without cardiovascular disease. By conducting a randomized controlled trial with varying SMS invitation lengths and reminder types, findings showed notably increased participation rates, especially with shorter messages and postal reminders. The study emphasizes the potential of combining digital approaches with traditional methods to enhance public health screening uptake, advocating for agile methodologies to adapt strategies based on real-time feedback for improved success rates.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]