"OpenAI has detailed a new internal engineering methodology called Harness engineering that leverages AI agents to drive key aspects of the software development lifecycle. The system uses Codex, a suite of AI agents, to perform tasks such as writing code, generating tests, and managing observability, based on declarative prompts defined by engineers. Harness standardizes workflows, reducing reliance on handcrafted scripts and custom tooling."
"In a five-month internal experiment, OpenAI engineers built and shipped a beta product containing roughly a million lines of code without any manually written source code. A small team of engineers guided agents through pull requests and continuous integration workflows. The work included application logic, documentation, CI configuration, observability setup, and tooling. Engineers provided prompts and feedback, while Codex agents iterated autonomously on tasks including reproducing bugs, proposing fixes, and validating outcomes."
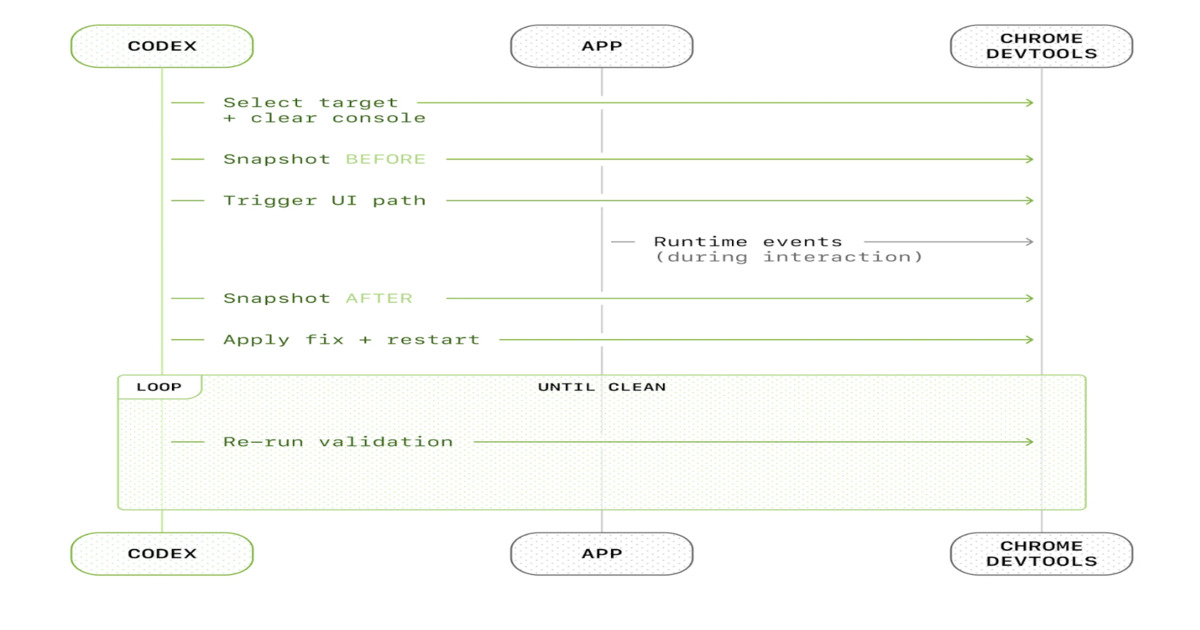
"Codex Agent‑Driven Application Testing and Feedback ( Source: OpenAI Blog Post) Harness engineering shifts human engineers focus from implementing code to designing environments, specifying intent, and providing structured feedback. Codex interacts directly with development tools, opening pull requests, evaluating changes, and iterating until task criteria are satisfied. Agents use telemetry, including logs, metrics, and spans, to monitor application performance and reproduce bugs across isolated development environments."
Harness engineering is an internal methodology that leverages Codex AI agents across the software development lifecycle to write code, generate tests, configure CI, and manage observability. Engineers declare intent and design environments while agents interact with development tools, open pull requests, run CI, reproduce bugs, propose fixes, and validate outcomes. A five-month experiment produced a beta product of roughly one million lines of code without manually written source files, guided by a small engineering team providing prompts and feedback. Agents ingest telemetry—logs, metrics, and spans—to monitor performance and reproduce issues across isolated environments. Internal documentation is organized in a structured docs directory with maps and execution plans.
Read at InfoQ
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]