"Since AlexNet5, deep learning has replaced heuristic hand-crafted features by unifying feature learning with deep neural networks. Later, Transformers6 and GPT-3 (ref. 1) further advanced sequence learning at scale, unifying structured tasks such as natural language processing. However, multimodal learning, spanning modalities such as images, video and text, has remained fragmented, relying on separate diffusion-based generation or compositional vision-language pipelines with many hand-crafted designs."
"Next-token prediction has revolutionized the field of language models1, enabling breakthroughs such as ChatGPT7 and sparking discussions about the early signs of artificial general intelligence8. However, its potential in multimodal learning has remained uncertain, with little evidence that this simple objective can be scaled across modalities to deliver both strong perception and high-fidelity generation. In the realm of multimodal models, vision generation has been dominated by complex diffusion models2,"
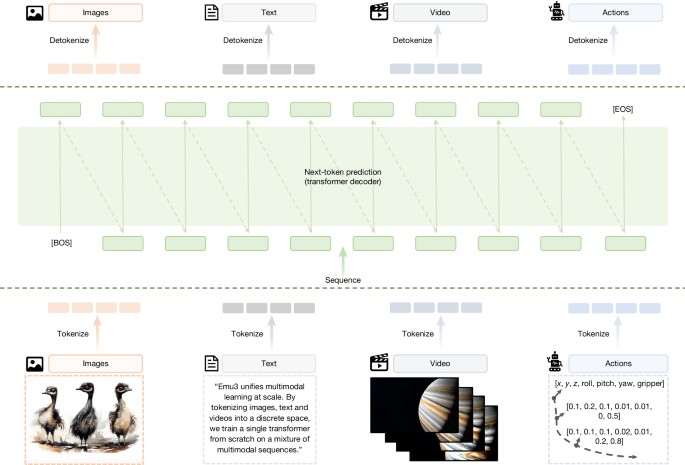
Deep learning replaced hand-crafted features by unifying feature learning with deep neural networks, and Transformers and GPT-3 advanced sequence learning at scale for structured tasks like natural language processing. Multimodal learning across images, video and text remains fragmented, typically using diffusion-based generation or compositional vision-language pipelines with many hand-crafted designs. Next-token prediction transformed language models, but evidence of its scalability across modalities for both perception and high-fidelity generation has been limited. Emu3 presents multimodal models based solely on next-token prediction, tokenizing images, text and videos into discrete representations to eliminate diffusion and compositional approaches while achieving competitive results.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]