#drug-development
#drug-development
[ follow ]
#clinical-trials #biotechnology #malaria #cancer-research #healthcare #biochemistry #alzheimers-disease
Medicine
fromFortune
1 week agoInside Big Pharma, VC's big bet on AI: 'We wouldn't fly in an airplane designed by hand, but all of our drugs are designed like that' | Fortune
AI-driven drug design aims to narrow the astronomical chemical search space and accelerate medicine development, backed by major funding and breakthroughs like AlphaFold.
fromHarvard Gazette
2 weeks agoHow COVID-era trick may transform drug, chemical discovery - Harvard Gazette
Laboratories turned to a smart workaround when COVID‑19 testing kits became scarce in 2020. They mixed samples from several patients and ran a single test. If the test came back negative, everyone in it was cleared at once. If it was positive, follow-up tests would zero in on who was infected. That strategy, known as group testing, saved valuable time, money, and resources.
Science
fromIPWatchdog.com | Patents & Intellectual Property Law
2 months agoInventing Miracles: How Patent Policy Shapes Drug Development | IPWatchdog Unleashed
In our latest IPWatchdog Unleashed podcast, I spoke with Rob Sahr, shareholder at Wolf Greenfield and co-chair of our 2025 Life Sciences Masters™ program. Our conversation zeroed in on a hard truth the public rarely sees: moving a molecule from early discovery to an FDA-approved therapy requires a chain of scientific and economic miracles-and every one of them leans on a reliable patent system.
Intellectual property law
#malaria
Public health
fromwww.bbc.com
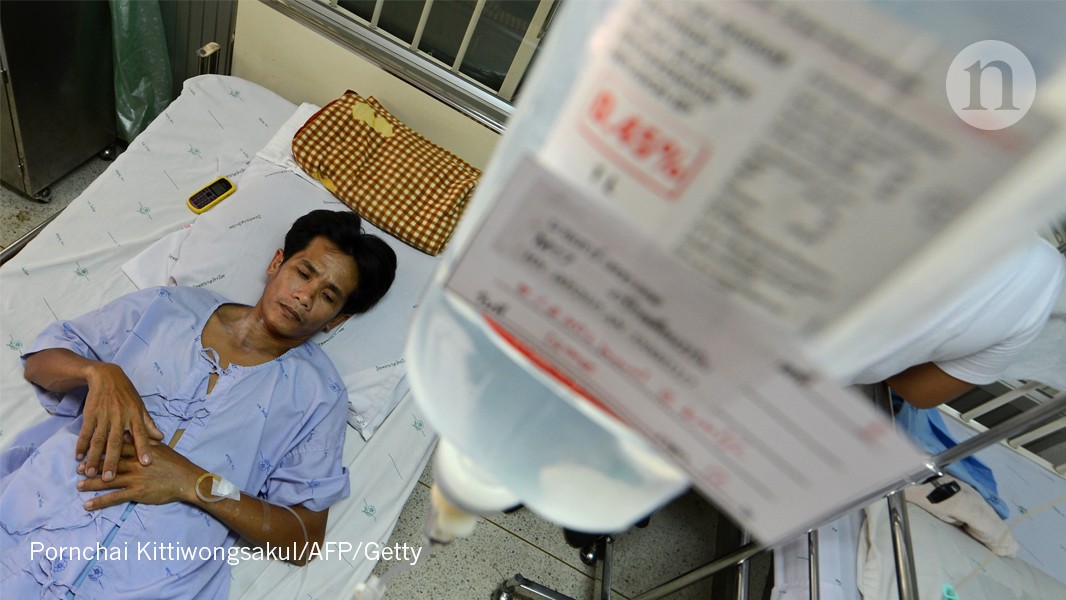
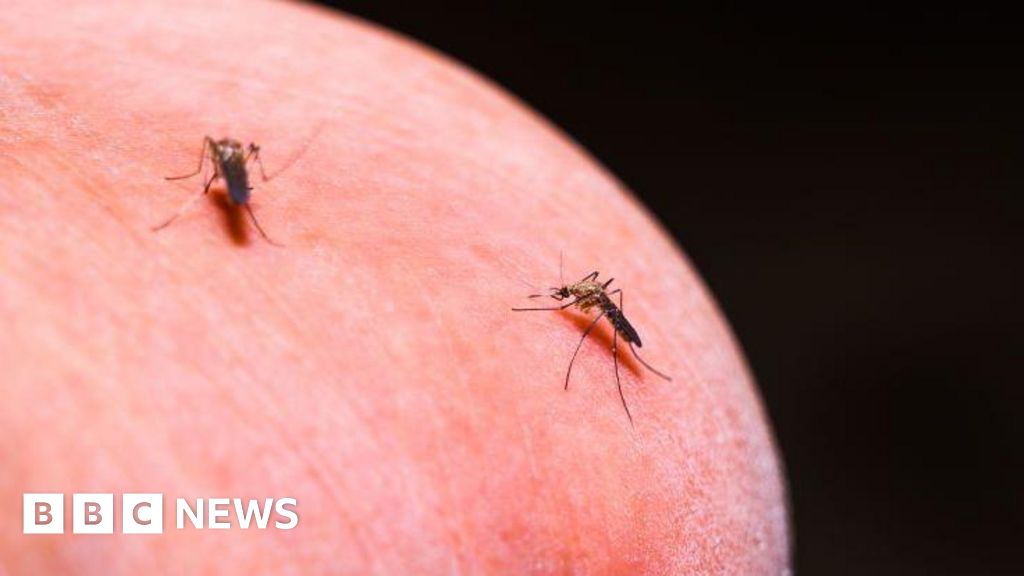
8 months agoScientists propose novel way of treating mosquitoes for malaria
US researchers propose using malaria drugs to cure mosquitoes instead of killing them, aiming to prevent disease transmission.
Coating bed nets with malaria drugs could effectively reduce parasite spread among mosquitoes.
fromThe Atlantic
2 months agoTrump's Animal-Research Plan Has a Missing Step
This year, the White House has broadcast its intent to greatly reduce animal experimentation in the United States. In early April, the Food and Drug Administration announced that it would require less testing on animals for the development of a widely used class of drugs-an approach, the agency says, that should speed up the drug-development process and eventually lower drug prices.
US politics
fromenglish.elpais.com
2 months agoHans Clevers, biomedical scientist: If I had colon cancer, I could grow my own tumor, test it with drugs, and see which one eliminates it'
Until now, preclinical trials relied primarily on two-dimensional cell cultures and animal models, which often failed to accurately replicate human biology. Since 2023, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not required animal testing, thanks in part to organoids, which Hans Clevers (Eindhoven, 68 years old), professor of molecular genetics at Utrecht University, has been researching since the beginning of the century.
Science
fromNews Center
3 months agoNew Study Gives Answers, Drug Targets for Chronic Lung-transplant Rejection - News Center
More than 50 percent of lung-transplant recipients experience a rejection of their new lung within five years of receiving it, yet the reason why this is such a prevalent complication has remained a medical mystery. Now, a new Northwestern Medicine study published in JCI Insight has found that, following transplant and in chronic disease states, abnormal cells emerge and "conversations" between them drive the development of lung damage and transplant rejection.
Medicine
fromInside Higher Ed | Higher Education News, Events and Jobs
4 months agoResearchers Map Out Possible Impacts of a Smaller NIH
Since the mid-1940s, the National Institutes of Health has sent billions of dollars to university researchers whose work has led to the creation of scores of lifesaving treatments for a range of diseases, including cancer, Alzheimer's and heart disease. By one estimate, NIH-funded research was linked to roughly 99 percent of drugs that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved between 2010 and 2019.
Science
fromwww.nytimes.com
5 months agoVideo: Opinion | America First? Not When It Comes to Your Health.
They hoped to make tomorrow's medicines. Then came Trump. This is Camila. She's trying to figure out how cancer spreads across the body. David here is trying to cure H.I.V. And Rachael, she's trying to find new treatments for childhood brain cancer. Or at least they were. The Trump administration has so far terminated more than $1 billion in grants for the National Institutes of Health. It has fired over 1,300 employees. 1,700 canceled awards.
Public health
fromenglish.elpais.com
6 months agoPedro Cuatrecasas, the scientist nobody has heard of who could have won two Nobel Prizes
Pedro Cuatrecasas was an influential biochemist who contributed to the development of approximately 40 drugs including acyclovir for herpes and atorvastatin for cholesterol management.
Science
fromNature
7 months agoFreeze frame: cracking molecular motion
Working on that timescale has long stymied biologists, but the rapid evolution of time-resolved cryo-electron microscopy (TR cryo-EM) over the past several years has made it possible to reconstruct dynamic processes with near-atomic detail.
OMG science
NYC politics
fromThe Nation
8 months agoInside the Bloodbath at the NIH
Trikafta's development exemplifies successful collaboration in American biomedical research between public and private sectors, transforming cystic fibrosis treatment.
The rapid FDA approval of Trikafta significantly improved treatment options for children with cystic fibrosis.
fromNews Center
9 months agoDistinguished Molecular Biologist Delivers 2025 Kimberly Prize Lecture - News Center
Evans' discovery of nuclear hormone receptors has transformed drug development, impacting treatments for diseases like diabetes and cancer, and underscoring the influence of biochemistry in medicine.
OMG science
[ Load more ]