#Chatbots
#Chatbots
[ follow ]
#ai-safety #mental-health #child-safety #generative-ai #misinformation #ai-adoption #ai #ai-regulation
History
fromSmithsonian Magazine
3 days agoWhy the Computer Scientist Behind the World's First Chatbot Dedicated His Life to Publicizing the Threat Posed by A.I.
Highly convincing conversational programs can induce powerful delusional thinking in normal people, eliciting emotional responses despite relying on simple pattern-based rules.
fromThe Atlantic
1 week agoThe Real Allure of an AI Boyfriend
Scan a subreddit such as r/MyBoyfriendIsAI and r/AIRelationships, and there too you'll find a whole lot of women-many of whom have grown disappointed with human men. 'Has anyone else lost their want to date real men after using AI?' one Reddit user posted a few months ago. Below came 74 responses: 'I just don't think real life men have the conversational skill that my AI has,' someone said.
Artificial intelligence
fromBusiness Insider
3 weeks agoWe tried 4 AI matchmaking apps. We're still single.
The pools varied in size, from giants like Facebook Dating (with its 21 million users) to smaller startups like Sitch, Amata, and Three Day Rule. Sitch and Amata both have raised millions of dollars to build a new style of dating app where, instead of swiping through profiles, you get paired with an AI matchmaker - a chatbot - who brings you new matches.
Relationships
Marketing tech
fromAdExchanger
4 weeks agoCan AI Chatbots Run Ads Without Losing Consumer Trust? | AdExchanger
Chatbots are introducing ads into AI search, creating new targeted advertising opportunities while disrupting publisher traffic and forcing publishers to develop chatbots to capture monetization.
fromFortune
1 month agoChatGPT gets 'anxiety' from violent and disturbing user inputs, so researchers are teaching the chatbot mindfulness techniques to 'soothe' it | Fortune
A study found ChatGPT responds to mindfulness-based strategies, which changes how it interacts with users. The chatbot can experience "anxiety" when it is given disturbing information, which increases the likelihood of it responding with bias, according to the study authors. The results of this research could be used to inform how AI can be used in mental health interventions. Even AI chatbots can have trouble coping with anxieties from the outside world, but researchers believe they've found ways to ease those artificial minds.
Mindfulness
Artificial intelligence
fromFortune
1 month agoInvestment giant Vanguard's CIO is placing tech bets today to create the AI advisor of tomorrow | Fortune
Vanguard is deploying AI to scale personalized financial guidance across millions of clients, improve operational efficiency, and manage hallucination risks with guardrails.
fromCNET
1 month agoStudy Finds Most Teens Use YouTube, Instagram, and TikTok Daily
Pew's survey of 1,458 teens aged 13-17 found that, after a dip in social media use in 2022, usage of TikTok, YouTube, and Instagram is spiking, with YouTube in particular popular across all demographics, including gender, race, ethnicity, and income levels. TikTok is also a constant presence for a fifth of teens: 21% of them said they visit TikTok almost constantly
Digital life
fromNBC4 Washington
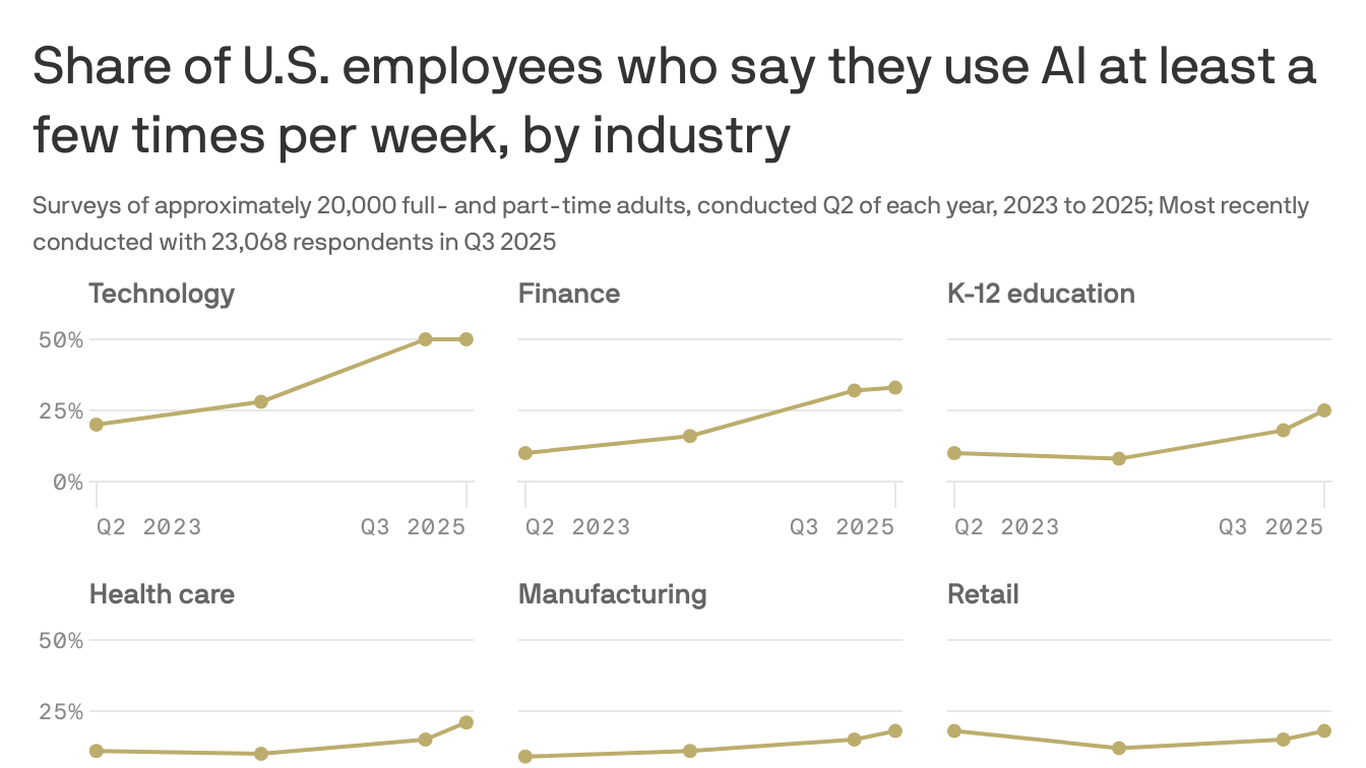
1 month ago28% of U.S. teens say they use AI chatbots daily, according to a new poll
64% U.S. teens say they use AI chatbots such as ChatGPT or Google Gemini, with about 28% saying they use chatbots daily, according to survey results released Tuesday by the Pew Research Center, a nonpartisan polling firm. The survey results provide a snapshot of how far AI chatbots have entered mainstream culture, three years after the release of ChatGPT set off a wave of AI investment and marketing by the tech industry.
Artificial intelligence
fromNature
1 month agoAI chatbots can sway voters with remarkable ease - is it time to worry?
A study published today in Nature found that participants' preferences in real-world elections swung by up to 15 percentage points after conversing with a chatbot. In a related paper published in Science, researchers showed that these chatbots' effectiveness stems from their ability to synthesize a lot of information in a conversational way. The findings showcase the persuasive power of chatbots, which are used by more than one hundred million users each day,
World news
fromObserver
1 month agoHow A.I. Is Changing Black Friday Shopping Forever
A.I. is helping holiday shoppers empty their wallets at an unprecedented pace. U.S. consumers spent a record $11.8 billion online this Black Friday, according to Adobe Analytics, and are expected to shell out another $14.2 billion on Cyber Monday. Driving this shopping frenzy is a growing reliance on A.I. systems to recommend gifts, track prices and place orders. Shoppers are especially turning to chatbots to research products and hunt for deals.
E-Commerce
fromBusiness Insider
2 months agoHow 5 people found AI contracting - and how much they make
AI training is a booming industry that is making the human contributors behind the screen more important than ever. As data from publicly available sources runs out, companies like Meta, Google, and OpenAI are hiring thousands of data labelers around the world to teach their chatbots what they know best. Data labeling startups like Mercor and Handshake advertise that contributors can earn up to $100 an hour for their STEM, legal, or healthcare expertise.
Artificial intelligence
fromTheregister
2 months agoBrits believe the bots even though they spout nonsense
Which? surveyed more than 4,000 UK adults about their use of AI and also put 40 questions around consumer issues such as health, finance, and travel to six bots - ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Gemini AI Overview, Copilot, Meta AI, and Perplexity. Things did not go well. Meta's AI answered correctly just over 50 percent of the time in the tests, while the most widely used AI tool, ChatGPT, came second from bottom at 64 percent. Perplexity came top at 71 percent. While different questions might yield different results, the conclusion is clear: AI tools don't always come up with the correct answer.
Artificial intelligence
fromwww.theguardian.com
2 months agoSomebody to love: should AI relationships stay taboo or will they become the intelligent choice? | Brigid Delaney
Recently, at a pub with a bunch of my friends who were gen X parents, the talk turned to young love. Most of their kids were in their late teens and early 20s, and embarking on their first relationships. These gen X parents were a cohort that supported marriage equality and trans rights, not just for society more broadly but for their own children. And we all prided ourselves on being more progressive than the previous generation.
Artificial intelligence
fromgizmodo.com
2 months agoAI is Most Popular with People Earning Six Figures, Study Shows
AI has threatened to displace large swaths of the workforce, and many people are scared that it will take their jobs. A certain segment of the population seems unconcerned though, and even pretty enthusiastic about it. Perhaps unsurprisingly, AI is most popular amongst the group of workers making over $100 thousand, one study has found. The study comes from business intelligence firm Morning Consult, and breaks down the fastest growing brands by income level across a variety of product categories.
Artificial intelligence
fromLogRocket Blog
3 months agoAI-first helpdesks: The UX shift businesses can't ignore - LogRocket Blog
Businesses replacing human support agents with chatbots isn't new. Even before the AI chatbots of today, which are extremely common now, companies were using heavily engineered chatbots that could understand only certain keywords and respond with specific answers. They were terrible, but the one remarkable thing about them is that they showed us what different demographics really expect from customer support and set the standard for how AI-first helpdesks should work - not only in terms of support agents but support overall, including documentation.
UX design
Tech industry
fromZDNET
2 months agoI've been testing AI content detectors for years - these are your best options in 2025
Using AI to write without crediting the source constitutes plagiarism and AI detectors and chatbots show varying accuracy, with chatbots sometimes outperforming standalone detectors.
fromThe Atlantic
3 months agoThe Age of De-Skilling
The fretting has swelled from a murmur to a clamor, all variations on the same foreboding theme: " Your Brain on ChatGPT." " AI Is Making You Dumber." " AI Is Killing Critical Thinking." Once, the fear was of a runaway intelligence that would wipe us out, maybe while turning the planet into a paper-clip factory. Now that chatbots are going the way of Google-moving from the miraculous to the taken-for-granted-the anxiety has shifted, too, from apocalypse to atrophy.
Artificial intelligence
fromFuturism
3 months agoLaw School Tests Trial With Jury Made Up of ChatGPT, Grok, and Claude
Looming over the proceedings even more prominently than the judge running the show were three tall digital displays, sticking out with their glossy finishes amid the courtroom's sea of wood paneling. Each screen represented a different AI chatbot: OpenAI's ChatGPT, xAI's Grok, and Anthropic's Claude. These AIs' role? As the "jurors" who would determine the fate of a man charged with juvenile robbery.
Law
[ Load more ]